Pancreatic cancer is a malignant tumor of digestive tract with high malignancy and difficult diagnosis and treatment. Among them, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) accounts for more than 95% of all pancreatic cancer.
In recent years, the incidence rate and mortality rate of pancreatic cancer have increased significantly. The early diagnosis rate of pancreatic cancer is not high, and it is often late when it is found. At this time, the cancer cells have spread. Although some chemotherapy drugs are effective, they usually produce drug resistance, and it is difficult for cancer immunotherapy to play a role. The 5-year survival rate of pancreatic cancer is less than 7%, and it is the malignant tumor with the worst prognosis. Therefore, it is also known as the "king of cancer".
According to the latest data of who, pancreatic cancer is the seventh cancer with the highest incidence in China in 2020 (120000 new cases are expected in 2020) and the sixth cancer with the highest death rate (120000 deaths are expected in 2020).
On June 2, 2022, the research team of New York University Grossman School of Medicine published a paper entitled "exercise induced engagement of the IL-15 / il-15r" in cancer cell, an international top oncology journal α Axis promotes anti tumor immunity in pancreatic cancer.
This study found that aerobic exercise can reprogram the immune system, inhibit the growth of pancreatic cancer and enhance anti-tumor immunity. This study also revealed the dependence of the anti-tumor and immune activation effects produced by exercise on the IL-15 signaling pathway.
This study demonstrated that pharmacological activation of IL-15 could improve the survival of mouse models and increase the sensitivity of pancreatic tumors to immunotherapy and chemotherapy. These findings identify a exercise / immune modality with clinical application potential for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.

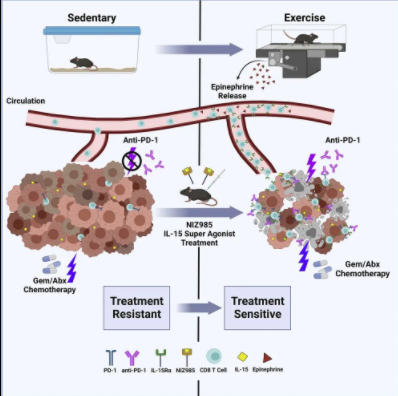
Exercise can promote the survival of CD8 T cells sensitive to IL-15 and double the number of tumor homing to pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) in mice. This effector T cell has been proved by other studies to be able to kill cancer cells.
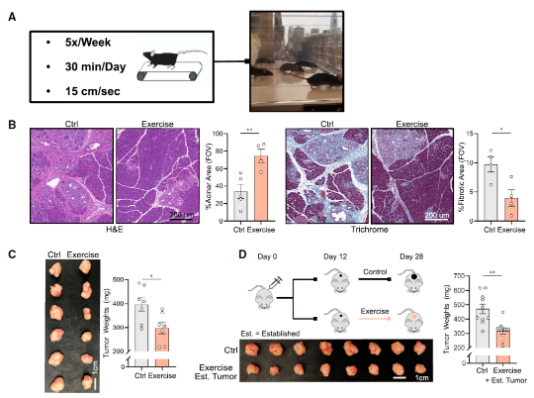
In this latest study, the research team used low-intensity treadmill running to simulate aerobic exercise, and let the mouse model with slowly progressing pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) perform low-intensity running for 30 minutes five times a week. The results showed that this kind of exercise effectively alleviated the tumorigenesis and reduced the tumor formation rate by 50%. In another group of mouse models, mice began to exercise 12 days after tumor transplantation, resulting in a 25% reduction in tumor weight. These results indicate that aerobic exercise can play an anti-tumor role in the tumor initiation stage and tumor progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Next, the research team cooperated with researchers from MD Anderson Cancer Center to verify in human pancreatic cancer patients. They found that those patients who exercised before pancreatic cancer resection had more CD8 effector T cells. These T cells expressed a protein called granzyme B (gzmB), giving them the ability to kill tumor cells. Another clinical trial started in 2017 showed that patients who exercised and had more CD8 effector T cells had a 50% higher 5-year survival rate.
Emma Kurz, the first author of the paper, said that this study shows for the first time how aerobic exercise affects the immune microenvironment in pancreatic tumors. This study helps to reveal that the activation of IL-15 signal transduction in pancreatic cancer may be an important therapeutic method in the future.
In the past few years, as the role of IL-15 signaling in tumors has become clearer, some researchers have tried to treat cancer by direct infusion of IL-15, but unfortunately, this increases the risk of systemic inflammatory damage. After that, some researchers began to focus on the receptor protein of IL-15 on the surface of T cells and NK cells - il-15r α。 IL-15 and il-15r α The relationship between them is like a key and a lock. There are new drug candidates that transfer information to activate target cells by imitating these "key and place" interactions.
Novartis, a pharmaceutical giant, has been developing a "super agonist" drug, niz985, aimed at enhancing IL-15 / il-15r α Pathway signaling, reducing the possibility of harmful inflammatory effects. However, this method has not been tested in a large number of patients with pancreatic cancer.
In this study, they found that both aerobic exercise and treatment with niz985, a super agonist developed by Novartis, can improve the effect of chemotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibitor (anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody).
The emergence of immune checkpoint inhibitors has changed the pattern of cancer treatment, but it has little effect on pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. In this study, they found that treatment with anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody alone could increase the number of il-15-sensitive and tumor killing CD8 + T cells in mouse pancreatic tumors by 66%. And increased by 175% when combined with exercise. In addition, the research team also found that the combination treatment of niz985, a super agonist of IL-15, and anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody can improve the survival rate of mice with advanced pancreatic cancer by 100%.
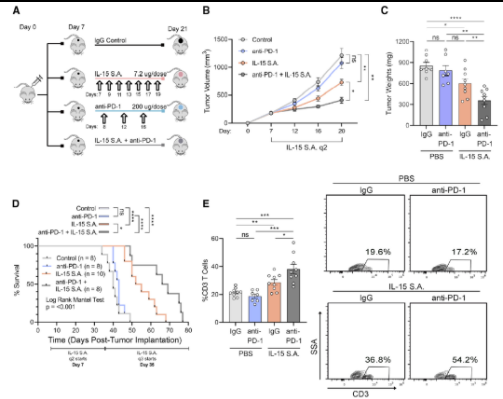
Dafna bar Sagi, the leader of the study, said that this study showed that exercise and related IL-15 signaling can improve the response of drug-resistant pancreatic cancer to immunotherapy. Even low-intensity exercise can profoundly change the tumor microenvironment, which also shows the potential of exercise in the treatment of pancreatic cancer, a fatal tumor.
It is reported that based on this research result, the research team is cooperating to carry out a human clinical trial to evaluate the immune effect of exercise on patients with pancreatic cancer. In addition, the research team also plans to continue to explore the effect of the combination of IL-15 super agonist and chemotherapy drugs in the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
Source link:
https://www.cn-healthcare.com/articlewm/20220815/content-1418096.html













