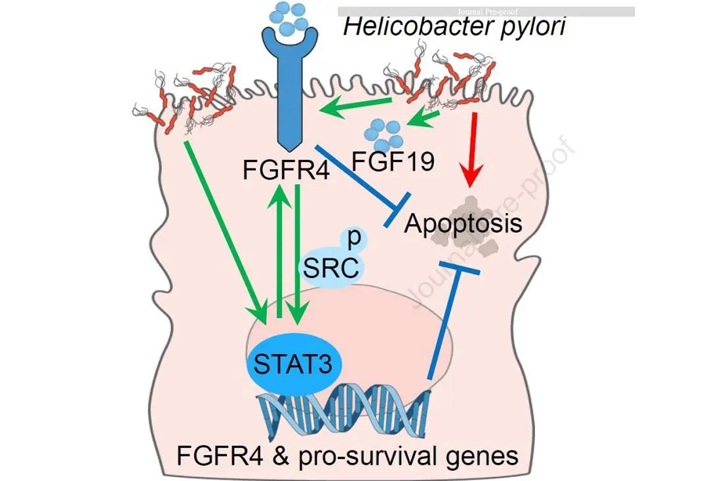
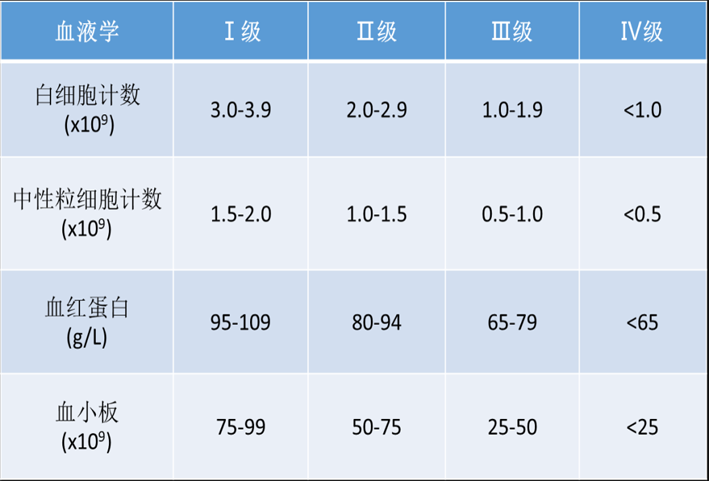
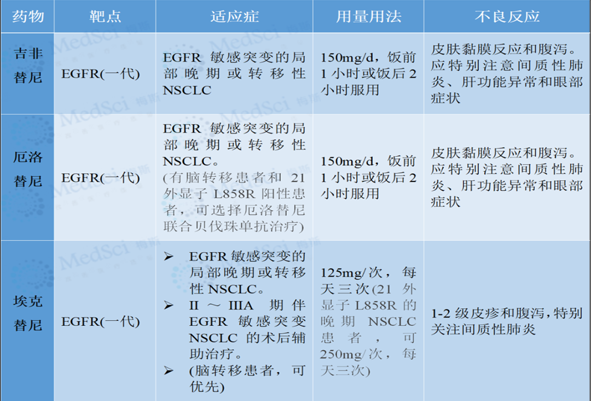
The report from the British research team pointed out that excessive use of antibiotics may increase the risk of colon cancer, especially in young people.

Sarah Perrott, a cancer researcher at the University of Aberdeen and co-author of the study, said: "This is the first study to associate antibiotic use with an increased risk of early-onset colon cancer - the disease has increased at least 3% annually in the past 20 years.".
The researchers compared the data of nearly 8000 people with colon and rectal cancer in Scotland with the data of people without the disease, and found that there was an association between the use of antibiotics and the increased risk of colon cancer in all age groups.
However, the study found significant age-related differences. The use of antibiotics increased the risk of colon cancer in people under 50 years old by nearly 50%, and the risk of colon cancer in the elderly increased by 9%.
In young people, antibiotic use is associated with cancer on the right side of the colon. Quinolones and sulfonamides/trimethoprim - antibiotics used to treat many infections - are associated with cancer.
Studies have not yet confirmed that antibiotics can directly lead to the occurrence of this type of cancer, and there is only correlation.
This research result will be released at the 2021 World Congress of Gastric Cancer (online conference) of European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO).
"Junk food, sugary drinks, obesity and alcohol are likely to play a role in the increase of colon cancer.
However, our data emphasize the importance of avoiding the use of antibiotics under unnecessary conditions.
Especially for children and young people, "Perrault said in a press release at a conference.
Dr. Leslie Samuel, the author, pointed out that: "The content on the right side of the colon is more mobile, and the natural bacteria (called microbiome) it inhabits may be different from the bacteria below the colon.
"At present, we need to know whether there is a link between the use of antibiotics and changes in the microbiome, and whether the incidence rate of colon cancer can be increased in young people.".
Samuel, an oncologist consultant at Aberdeen Royal Hospital, also said that this was a complex challenge. This is because even when the colon is cleared for diagnostic procedures such as endoscopy, the microbiome can quickly return to its previous state.
"We don't know whether antibiotics can have any direct or indirect impact on the microbiome that can lead to the development of colon cancer," Samuel said.
Research presented at meetings is generally considered preliminary until published in peer-reviewed journals.
Source:
Reference link:
https://www.cn-healthcare.com/articlewm/20220925/content-1441016.html