Cancer is one of the leading causes of death in the world, but its burden in various countries and regions is not consistent. The cancer burden in both developed and developing countries has increased over time for complex reasons, including population aging and population growth, accelerated socio-economic development and changes in the prevalence of related risk factors. With population growth and global aging, cancer has become the main cause of premature death and reduced life expectancy in many countries.
In recent years, the cancer burden in the United States is gradually decreasing. China's cancer is changing. The incidence rate of cancer is higher. It has already surpassed the US. China's cancer mortality rate is far more than that of the United States. By comparing the latest cancer profiles, trends and determinants between China and the United States, learning from the progress made in cancer prevention and care in the United States and measures to actively respond to population aging, it will help China reduce the burden of cancer.
Recently, Professor Chen Wanqing's team from the National Cancer Center of Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences published a paper entitled cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: profiles, trends, and determinations in the English edition of Chinese Medical Journal.

This paper uses open source data for comparative research, and uses 2020 global cancer burden data and United Nations population data to estimate the new cancer cases and deaths in 2022. The trend of cancer incidence rate and mortality in the United States has been used by the SEER database of the National Cancer Institute of the United States and the National Center for health statistics. Chinese data are from the cancer registration report.
In 2022, China and the United States will have about 4820000 and 2370000 new cancer cases and 3210000 and 640000 cancer deaths, respectively. In other words, the number of new cancer cases in China is about twice that of the United States, but the number of deaths is about five times that of the United States.
The most common cancer in China is lung cancer, while in the United States it is breast cancer. But lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in both China and the United States.
With the popularity of prevention and screening technology, the incidence rate and mortality rate of lung cancer and colorectal cancer in the United States have decreased significantly recently, but the incidence rate of liver cancer has increased slightly.
In China, incidence rate of gastric cancer, liver cancer and esophageal cancer has been decreasing, but the incidence rate of colorectal cancer, male prostate cancer and seven other kinds of female cancers has increased.
The data show that the increase of adult population and population aging are the main determinants of the increase of cancer deaths.
The burden of liver cancer, gastric cancer and esophageal cancer is decreasing, and the burden of lung, colorectal, breast and prostate cancer is increasing, which means that the cancer situation in China and the United States is converging. Population ageing is a growing determinant of the increased burden of cancer. The progress made in cancer prevention and care in the United States and the measures to actively respond to the aging population are worthy of our reference to help China reduce the burden of cancer.
Trends in cancer incidence rate and mortality
Figure 1 shows the long-term trend of incidence rate and mortality rate of 10 main cancer types in both sexes. They are men: lung cancer, stomach cancer, colorectal cancer, liver cancer, esophageal cancer, prostate cancer, pancreatic cancer, bladder cancer, leukemia, brain and central nervous system cancer. Female: breast cancer, lung cancer, colorectal cancer, thyroid cancer, gastric cancer, liver cancer, esophageal cancer, cervical cancer, uterine cancer, brain and central nervous system cancer.

Figure 1
In men, the incidence rate and mortality rate of lung cancer and colorectal cancer in China, and gastric cancer, liver cancer and esophageal cancer in China have been decreasing in recent years. However, the incidence rate of liver cancer, China's colorectal cancer and prostate cancer has increased significantly.
The incidence rate of prostate cancer in the United States increased sharply in the early 1990s due to extensive screening for prostate specific antigen. From 2007 to 2014, the incidence rate of prostate cancer in the United States dropped rapidly, and the mortality rate of prostate cancer increased slightly in the early 1990s.
In women, the incidence rate and mortality rate of lung cancer and colorectal cancer in China, and gastric cancer, liver cancer and esophageal cancer in China have been decreasing in recent years. However, since 2000, the incidence rate of the seven other most common cancers in China has increased.
It is worth noting that the incidence rate of thyroid cancer has increased dramatically since 2000, China and the United States, but the mortality rate is very stable during this period.
Determinants of cancer death
Based on the number of cancer deaths in 1990 as the baseline, the increased number of deaths between 1991 and 2019 is represented by four decisive factors. The proportion of all cancer deaths attributed to the four determinants per year is shown in Figure 2.
The increase in the size of adults aged 25 and over is the main determinant of the increase in cancer deaths in China and the United States. Since 2005, population aging has been the second determinant of the increase in cancer deaths, which may exceed the impact of the increase in population size in the future. In addition to male men, the incidence rate of cancer at certain ages increases the number of cancer deaths. However, the proportion of deaths associated with specific age cancer is far below the proportion of deaths associated with population size and population ageing, and the gap is rapidly expanding. In recent years, China has made a greater contribution in this regard than the United States.
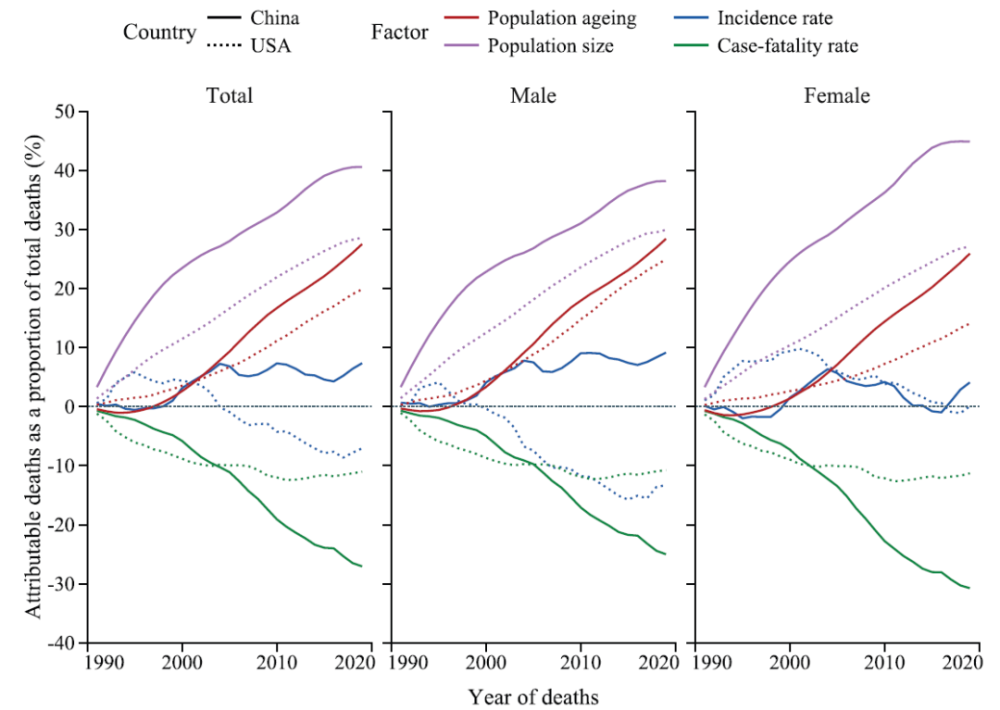
Figure 2
Comparison of cancer between China and the United States
In this comparative study, the Chen Wanqing team reported the estimated cancer statistics in 2022, the long-term trend of cancer incidence rate and mortality rate, and the determinants of the increase in cancer deaths in China and the United States.
Lung cancer is still the most common cancer in China in 2022, and the most common cause of cancer deaths in China and the United States. Breast cancer is the most common cancer in the United States in 2022. With the incidence rate incidence and mortality of gastric cancer, liver cancer and esophageal cancer decreasing, and the incidence rate of lung cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer and prostate cancer increasing, the cancer situation in China is becoming similar to that in the United States.
The increase in the size of the adult population and population aging are the main determinants of the increase in cancer deaths. Some achievements in cancer prevention in the United States may provide reference and help for the development of China's cancer control strategy.
In the foreseeable future, population aging is likely to become one of the main social characteristics of China. China is one of the countries with the fastest aging population growth in the world. By the end of 2020, China has 260 million people aged 60 and over, which is expected to increase by about 10 million annually from 2021 to 2025. It is estimated that China's total population will peak around 2025, and the proportion of people aged 60 and above is expected to exceed 30% by 2035. If the population size remains stable or decreases, but the population aging continues to intensify, the upward trend of China's cancer burden may remain unchanged. Therefore, it is necessary to integrate healthy aging strategies into cancer prevention and strengthen multisectoral cooperation in policy formulation.
China is changing to the cancer characteristics of developed countries, characterized by high incidence rate of lung cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer and prostate cancer. These changes are driving large-scale cancer screening and early detection for eligible people aged 45 to 74. The United States has developed several screening technologies and strategies to reduce the cancer burden and may be introduced into China's cancer screening services. Screening should be directed at high-risk groups and cancer, such as colorectal cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, cervical cancer and upper gastrointestinal cancer. Considering the large population, the potential benefits and hazards of screening and the capacity of health services, it is difficult for China to provide "one size fits all" cancer screening services in each province and county in the short term. Organized screening for high-risk areas and opportunistic screening for non-high-risk areas may be the most feasible solution in the near future.
In China, about 45% of cancer deaths in adults aged 20 and over can be attributed to 23 modifiable risk factors. Primary cancer prevention, which focuses on controlling behavioral, dietary, metabolic and environmental factors and infectious sources, has great potential in reducing the cancer burden in China.
The smoking rate of American adults gradually decreased from 25% in 1997 to 15% in 2015, while the smoking rate of Chinese adults has remained at 25% in recent years. Among Chinese adults aged 30 and over, about 16.8% of cancer deaths are attributed to active smoking and second-hand smoke.
With the vaccination of HPV vaccine, we see the hope of eliminating cervical cancer all over the world. However, since 2000, the incidence rate and mortality rate of cervical cancer in China have increased significantly. Therefore, China needs to adopt comprehensive strategies, including the promotion of HPV vaccination, cervical screening, preinvasive lesions and invasive cervical cancer treatment, which is expected to eradicate cervical cancer in the late 2040s.
In China, the 5-year relative survival rate of cancer increased from 30.9% in 2003-2005 to 40.5% in 2012-2015. However, the survival rate of specific cancer types in China is lower than that in the United States, especially in breast and colorectal cancer. The data of the research report also shows that the prognosis of cancer in China is worse than that in the United States. China needs to make more efforts to provide effective cancer treatment schemes and improve national health coverage.
China's incidence rate of incidence of colorectal cancer, female breast cancer and male prostate cancer has increased significantly, and the incidence rate of gastric cancer, liver cancer and esophageal cancer has been decreasing. This leads to a narrowing of the overall situation of cancer in China and the United States.
In view of the increasing cancer burden caused by the rapid aging of China's population, the progress made in cancer prevention and care in the United States and the measures to actively respond to the aging of the population are worthy of our reference to help China reduce the cancer burden.
Source: Tencent