With the popularization of CT screening for lung cancer, the detection rate of ground glass nodule (GGN) in the lung has gradually increased. What should a doctor do if a patient comes to consult with a chest CT? Follow up or further examination?
Lung GGN refers to the increased density shadow in the lung with clear or unclear boundary on CT, and its lesion density is not enough to cover up the vascular and bronchial shadow.
Pulmonary ground glass nodules can be divided into simple ground glass nodules (pggn) and mixed ground glass nodules (mggn) according to the uniformity of the internal components of the nodules.
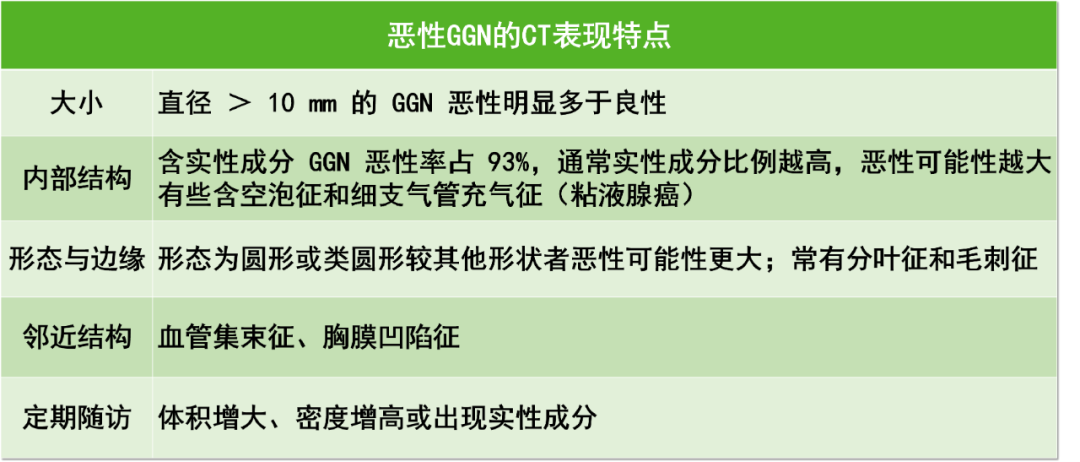
What are the characteristics of malignant pulmonary ground glass nodules?
1、 Follow up of pulmonary ground glass nodules
There was no obvious malignant sign in pulmonary nodules, and the size of solid nodules and some solid nodules was less than 8mm; If the pure ground glass nodule is less than 10mm, the nodule changes can be observed through regular follow-up. If there is progress, local nodule 1024ct target scanning (the coincidence rate with pathology can be as high as 95%) or nodule puncture can be performed. If there is no significant change, follow-up observation should be continued.
For pulmonary ground glass nodules <6mm, chest CT can be reexamined after 1 year. If the nodules are enlarged or the solid components are increased, chest CT can be reexamined after 3~6 months;
The diameter of the lesion is between 6~10mm. It is recommended to reexamine the chest CT after half a year. If it is enlarged or becomes solid and has malignant signs, surgical treatment should be considered;
For lesions larger than 10mm, the follow-up time will be shortened to 3-6 months. If the lesions are enlarged or become solid and have malignant signs, surgery will be considered.
1. Simple GGN
Kakinuma et al. Analyzed 7294 patients screened by CT from 2004 to 2007, and found 439 simple ggns with diameter ≤ 5 mm. During the follow-up of >5 years, only 45 (10.3%) increased, and only 4 (0.9%) of them developed into adenocarcinoma (2 cases of microinvasive adenocarcinoma and 2 cases of invasive adenocarcinoma). The average time of solid components in these 4 patients was 3.6 years. It indicates that short-term follow-up is not required for simple GGN <6mm.
Yankelevitz et al. Used CT to screen 57496 patients, including 2392 cases (4.2%) of simple GGN. 73 cases of adenocarcinoma were diagnosed in simple GGN. The median time from discovery to treatment was 19 months. The median time from simple GGN to mixed GGN was 25 months. After 78 months of follow-up, the postoperative survival rate of lung cancer patients was 100%, indicating that simple GGN of any size can be safely followed up at 12-month intervals. At the same time, studies have shown that simple GGN ≥ 6mm can be safely followed up. Its growth is slow, and it usually takes 3 to 4 years to grow up or add solid components.
2. Mixed GGN
Fleischner guidelines recommend that routine follow-up should not be performed for isolated mixed GGN <6mm. In clinical practice, it is difficult to judge whether there is solid component in such a small nodule, so follow-up is usually not required.
For mixed GGN ≥ 6mm, if the actual composition is <6mm, it is recommended to follow up every year for at least 5 years. Although mixed GGN has a higher possibility of malignancy, nodules with solid components <6mm are usually in situ adenocarcinoma or microinvasive adenocarcinoma, rather than invasive adenocarcinoma. The 5-year survival rate after resection is 100%. If the solid component is ≥ 6mm, short-term follow-up is recommended to confirm its continued existence and early intervention. More and more studies have shown that the larger the solid component, the greater the risk of invasion and metastasis, and its clinical manifestations and prognosis are more similar to those of solid nodules.
2、 Timing of intervention for pulmonary ground glass nodules
When to intervene in GGN depends mainly on the size of GGN, the size of solid components and dynamic follow-up changes.
Some 5 ~ 10mm GGN in clinical work can be actively intervened:
Peripheral GGN close to visceral pleura: local excision;
High risk factors: previous history of malignant tumor, family history, long-term smoking history;
There were signs of malignant tumor in imaging: lobulated sign, prickle sign, pleural depression and partial consolidation;
Positron emission tomography / computed tomography (PET-CT) showed increased metabolism;
The patient was extremely anxious about GGN and could not be relieved.
Some 5 ~ 10mm GGN shall be handled carefully:
GGN is located in the lung parenchyma and cannot be removed locally;
Pure GGN without dynamic follow-up;
Partial solid GGN, but no malignant signs in imaging, or no metabolism or low metabolism in PET-CT;
Old age, poor general condition;
Multiple GGN.
3、 Mistaken diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary ground glass nodules
Application of antibiotics: Khokhar et al. Studied 293 cases of small nodules and divided them into two groups according to whether to use antibiotics. The results showed that the remission rates of small nodules with and without antibiotics were 33% and 27% respectively, with no significant difference. There was no significant difference in remission rate among subgroups with pulmonary symptoms or CT signs of infection.
PET-CT examination: PET-CT has no diagnostic value for small pure GGN. For 8 ~ 10mm partial solid GGN, it is recommended to perform PET-CT examination before traumatic examination.
Close to the pleura, GGN is easy to spread in the pleural cavity: studies have shown that pure GGN will not invade the visceral pleura, so there will be no risk of spread in the pleural cavity.
4、 Surgical treatment of pulmonary ground glass nodules
Lobectomy is still the first choice for the treatment of lung cancer, and it can also achieve satisfactory results in the treatment of GGN. However, the application of sub lobectomy in the treatment of GGN has attracted more and more attention. Some studies have shown that sub lobectomy can achieve a similar prognosis as lobectomy for nodules with simple GGN components; However, for GGN with more solid components, sub lobectomy is still controversial.
The preliminary results of the prospective randomized controlled clinical trial jcog0802 have been published. Compared with lobectomy, except for slightly more blood loss (50 and 44.5ml respectively), higher chest tube replacement rate (3.8% and 1.4% respectively) and slightly higher incidence of alveolar pleural fistula (9% and 7% respectively), the short-term effects of lobectomy and lobectomy are similar.
Case discussion:
Female, 47 years old.
In September, 2021, a physical examination revealed a nodule of about 14mm in the lower lobe of the left lung.
CT was also performed in july2018. Compared with 2018, CT in 2021 showed an increase in nodules and solid components.
In October, 2021, the detection results of a full set of lung cancer tumor markers were normal.
CT thin-layer plain scan will be performed in February 2022. The pulmonary nodules were enlarged by 0.5mm.
In March, 2022, the results of 7 antibody tests of lung cancer were normal.
Thin slice CT image of chest in February 2022:

The main lesion is located in the left lower lobe. It is mainly composed of solid components (pink arrow), a little ground glass components (green arrow) at the edge, with burr traction (blue arrow). The lesion is clearly divided into leaves (brick arrow), and the local edges are particularly neat (yellow arrow, interlobular septum?).
CT images in july2018:

On the surface above, it is obviously a mixed ground glass lesion with clear outline, lobulated (brick arrow), clear tumor lung boundary, and significant ground glass components (green arrow), and solid components (pink arrow) at that time, and the density is not low. The feeling is consistent with malignancy.
Compared with the films in july2018 and february2022, the lesions were already a typical manifestation of invasive adenocarcinoma when they were first found, and they were significantly progressive and solid after follow-up. Therefore, the possibility of chronic inflammation and granulomatous inflammation can be basically ruled out after comparison. Therefore, it is not recommended to continue the follow-up, and surgical treatment should be performed.
In conclusion, the timing of surgery is mainly determined by the size of the nodule, the size of solid components and dynamic follow-up changes. Subpulmonary lobectomy of GGN is being accepted by more and more doctors, but we still need to wait for the long-term follow-up results of prospective randomized controlled trials.
Article source:
https://www.medsci.cn/article/show_article.do;jsessionid=91A007052BE2AE02FEDA9862AC69ECC5?id=f668e2886658