Nausea and vomiting is a common adverse reaction of tumor drug therapy, also seen in non-specific treatment. Nausea and vomiting in advanced tumors are common, often accompanied by anorexia, pain, anxiety, fatigue, depression, dyspnea, etc., which can cause dehydration, nutritional deficiency, inhalation pneumonia, electrolyte disorder, asphyxia, and even death.
Non therapeutic nausea and vomiting in advanced tumors refers to nausea and vomiting caused by specific treatment (such as radiotherapy and chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, surgery), such as brain metastasis, increased intracranial pressure, use of opioids, intestinal obstruction, etc. The Expert Consensus on Non therapeutic Nausea and Vomiting in Advanced Tumor Patients (2022) recommended that its treatment strategies mainly include etiological treatment and empirical drug treatment. Etiological treatment includes gastrointestinal decompression, gastrostomy, surgery to relieve vomiting caused by intestinal obstruction, and abdominal catheter drainage; Reduce abdominal pressure and relieve nausea and vomiting caused by malignant ascites; Glucocorticoid treatment of vomiting caused by increased intracranial pressure. For empirical drug treatment, first select a class of antiemetic drugs, and replace or use other drugs in combination if ineffective.
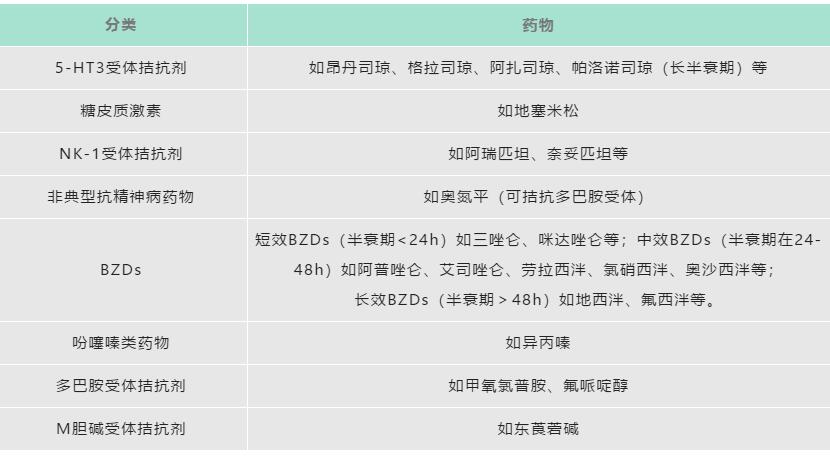
Antiemetic drugs are commonly used for non therapeutic nausea and vomiting. According to different mechanisms of action, they can be divided into 5-HT3 receptor antagonists, glucocorticoids, NK-1 receptor antagonists, atypical antipsychotics, dopamine receptor antagonists, benzodiazepines (BZDs), phenothiazines, and M-choline receptor antagonists (see Table 1 for details).
Table 1 Common antiemetic drugs
I Drug use of non therapeutic nausea and vomiting in patients with advanced cancer
Dopamine receptor antagonists such as metoclopramide and anti dopamine drugs (such as haloperidol and olanzapine) are the first choice for the treatment of non treatment related nausea and vomiting in advanced tumors. Those who do not respond to first-line drugs may consider replacing or combining 5-HT3 receptor antagonist and NK-1 receptor antagonist, and glucocorticoid can be used as a substitute. Glucocorticoid dexamethasone can be used for nausea and vomiting caused by brain metastasis or intestinal obstruction.
(1) 5-HT3 receptor antagonist
5-HT3 receptor antagonist is effective in antiemetic, and is often used to prevent nausea and vomiting caused by radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
Ondansetron is used for patients with moderate to severe liver function ≤ 8mg/d. Granisetron, ondansetron and dorasetron can cause fatal arrhythmia and prolong QT interval. It should be used cautiously for congenital long QT syndrome, cardiac conduction interval, especially those with prolonged QT interval.
(2) Dopamine receptor antagonist
Metoclopramide, a dopamine receptor antagonist, has an effective antiemetic effect and is commonly used to prevent nausea and vomiting caused by radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
Metoclopramide can cause extrapyramidal reaction, hyperprolactinemia, lactation, breast pain, irregular menstruation, etc. It should not be used in patients with mechanical intestinal obstruction or perforation or gastrointestinal bleeding.
(3) NK-1 receptor antagonist
NK-1 receptor antagonist plays a strong antiemetic effect by blocking substance P, and can be used to treat nausea and vomiting caused by acute and delayed radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
Those who use cisapride, pimozide, terfenadine and astemizole should not use alepidem.
(4) Glucocorticoid
For example, dexamethasone is effective in controlling acute and delayed CINV, reducing intracranial pressure and edema, and can be used for vomiting caused by increased intracranial pressure.
It can cause hypokalemia, gastrointestinal bleeding, hyperglycemia, osteoporosis, infection, etc. It is forbidden to use it in the infected people who have recently undergone gastrointestinal anastomosis, active ulcers, severe osteoporosis, and uncontrollable antimicrobial therapy.
(5) Antipsychotic drugs
In the late stage of tumor nausea, sedatives can be used, such as olanzapine and haloperidol.
Olanzapine has mood stabilizing and anti anxiety effects, can be used to prevent acute and delayed CINV, and can rapidly improve nausea, anorexia and fatigue. It can cause abnormal blood glucose and lipid, dizziness, hypotension, leukopenia, joint pain, etc. It should not be used for people with known risk of narrow angle glaucoma.
Haloperidol has strong antiemetic effect, can also calm down, and can be used to treat nausea and vomiting. It can cause Q-T interval prolongation, tachycardia/bradycardia, abnormal blood pressure, extrapyramidal reaction, grand seizure, hyperprolactinemia, dyskinesia, etc. It is forbidden to use in patients with basal ganglia disease, Parkinson's syndrome, Parkinson's disease, myelosuppression, severe central nervous suppression, myasthenia gravis, and glaucoma.
II Drugs for nausea and vomiting caused by intestinal obstruction unsuitable for surgery
Pelvic or abdominal tumors, such as advanced ovarian tumors or gastrointestinal tumors, are prone to malignant intestinal obstruction, which is characterized by persistent nausea, intermittent vomiting, abdominal colic, and abdominal distension, and is not suitable for surgical treatment.
The initial treatment for patients with intestinal obstruction who are not suitable for surgery can choose anti secretions and antiemetic drugs. Antisecretory drug octreotide combined with antiemetic drugs (such as granisetron and metoclopramide) can be selected. If the above treatment fails, the anticholinergic drug scopolamine combined with antiemetic drugs can be considered.
(1) Antisecretory agent
Severe vomiting still occurs after using antiemetic drugs. Antisecretory drugs such as scopolamine butylbromide or octreotide can be used together.
Scopolamine is an anticholinergic drug, which can relieve spasm and vomiting, and can be used to treat fulminant/refractory nausea and vomiting. It can cause dry mouth, dizziness, skin flushing, burning, irritability, excitement, convulsion, delirium, visual adjustment disorder, lethargy, palpitations, headache, dilated pupils, etc. Organic pyloric stenosis, severe heart disease, paralytic intestinal obstruction and glaucoma are prohibited. Use with caution in patients with enlarged prostate.
Octreotide is a somatostatin analogue, which can improve the degree of nausea and vomiting caused by intestinal obstruction and significantly reduce the secretion of digestive tract. It is recommended as the first-line drug for nausea and vomiting caused by malignant intestinal obstruction. It can cause diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, constipation, gastrointestinal flatulence, cholelithiasis, headache, dizziness, hyperglycemia, fatigue, hypoglycemia, etc. Patients with cholelithiasis and abnormal pancreatic function should be cautious.
(2) Antiemetic drug
It is suggested that antiemetic drugs should be those with multiple mechanisms of action. If one drug cannot fully control nausea and vomiting, drugs acting on different receptors should be selected.
Dopamine receptor antagonists generally have both antiemetic and gastrointestinal motility effects. Metoclopramide can promote gastric emptying, enhance gastrointestinal motility, improve nausea and vomiting, can be used for early and partial intestinal obstruction, and avoid complete obstruction or colic. Sehaloperidol can be used in complete obstruction or colic, which can improve nausea and vomiting in incomplete intestinal obstruction.
Glucocorticoids such as dexamethasone can be used together with antiemetic and anti secretory drugs to relieve nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain, and its combination with ranitidine can be used to reduce gastrointestinal secretion.
Olanzapine can combine with a variety of neurotransmitters such as 5-HT, dopamine, taurine, adrenaline, etc. to stop vomiting and effectively improve nausea and vomiting in incomplete intestinal obstruction.
III Drug induced nausea and vomiting
Drugs such as opioids, antibiotics, antifungal drugs, anticonvulsants, digoxin, iron, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), dopamine agonists, tricyclic antidepressants, and non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can cause vomiting, among which the vomiting caused by opioids, antibiotics, anticonvulsants, digoxin, iron, and NSAIDs can be well reversed. Opioids are commonly used as analgesics for advanced tumors. Nausea and vomiting caused by opioids can be tolerated after 5-7 days, and some of them may persist. Antiemetic drugs can be 5-HT3 receptor antagonists, NK-1 receptor antagonists, and oxazone.
Reference:
1.晚期肿瘤患者非治疗性恶心呕吐中西医治疗专家共识[J].中国中医急症,2022,31(9):1317-1323.
2.化疗所致恶心呕吐的药物防治指南[J].中国医院药学杂志,2022,42(5):457-469.
3.肿瘤药物治疗相关恶心呕吐防治中国专家共识(2019年版)[J].中国医学前沿杂志,2019,11(11):16-24.
4 .2014版中国麻醉学指南与专家共识[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2014:305-310.
5.陈奇等.苯二氮䓬类药物在老年人群中应用现状研究进展[J].中华医学杂志,2021,101(35):2817-2819.
6.中国肺癌脑转移诊治专家共识(2017年版)[J].中国肺癌杂志,2017,20(1):7-8.
Article Source:
https://www.medsci.cn/article/show_article.do?id=db42e4491589