On June 4, 2021, the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), an annual event of the global oncology community, officially kicked off, and many top research results at home and abroad will be announced soon. Mace medicine will continue to pay attention to and report academic highlights, and share them with you.

In this article, mace medicine has sorted out the heavy research on gastrointestinal tumors at home and abroad, and shared it with you.
1. Molecular characteristics of long-term and short-term survivors of advanced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Due to the lack of effective screening methods and early diagnosis methods, most patients are locally advanced and metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), and the median overall survival of patients with advanced PDAC is less than 1 year.
Some studies have shown that although the prognosis of patients with advanced PDAC is still not ideal, compared with untreated patients, the median overall survival of patients receiving chemotherapy can be prolonged by about 2 times. Some patients develop rapidly, which also means that PDAC has biological heterogeneity. Therefore, it is very important to understand the biological differences of PDAC.
The researchers collected the electronic medical records of patients with locally advanced or metastatic PDAC from compass (nct02750657) and pog/pangen (nct02155621, nct02869802). The patients' ECoG PS was 0-1. The chemotherapy regimen was based on the preference of clinicians, and hrdetect was used to identify homologous recombination defects. The biological characteristics of patients with very short overall survival (STS) (≤ 3 months) and long overall survival (LTS) (≥ 24 months) were compared.
The results showed that 341 patients were included in the analysis, including 47 STS (MOS 1.6 months) and 42 lts (MOS 29.7 months). There were no differences in median age, BMI, or gender between cohorts. STS is more likely to have ECoG PS 1 vs 0, higher tumor burden (RECIST) and higher CA19.9 at the time of diagnosis.
In STS, 71% of patients had an inestimable response due to clinical decline or death before the first scan, and 28% of PD was the best response. In LTS, the orr of chemotherapy was 69%. 64% and 33% of lts and 32% and 36% of STS received mffx and GA, respectively. There was no difference in the incidence of KRAS mutations (90% vs 98%) or specific mutant alleles, but amplification of mutant KRAS was more common in STS (35% vs 65%, p=0.01).

The incidence of inactivation driven mutations (17% vs 30%, none) in TP53, CDKN2A and Smad4 (90% vs 98%) and genes involved in chromatin modification (arid1a, smarca4, pbrm1, kdm6a) was similar in the two groups. However, STS has a high mutation rate, resulting in the activation of pi3k/akt/mtor pathway. However, in LTS, 6/7 were the result of germline pathogenic variation, while in STS, only 1/5 were. The tumor structure variation load, TMB and substitution base characteristics were similar in the two cohorts.
In conclusion, the survival time of patients with advanced PDAC is ≤ 3 months, which is characterized by heavy tumor burden, consistent molecular spectrum with enhanced RAS signal transduction, imbalance of pi3k/akt/mtor pathway and basal transcriptome subtypes. HRD genes are heterogeneous, and lts carries some HRD genes.
2. CtDNA detection can detect the recurrence risk of gastric cancer earlier
Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) is a tumor derived fragment of DNA in the blood, which is a characteristic tumor marker. The trace information of tumor in the patient's blood can be detected by ctDNA detection. At present, ctDNA detection has become a potential prognostic marker for various tumor types, including gastric cancer patients.
The researchers recruited 100 patients with stage ii/iii resectable gastric cancer (nct02887612) from October 2016 to June 2019. Primary tumor and plasma samples were collected during the perioperative period and after adjuvant chemotherapy (ACT). Somatic mutations were captured by targeted sequencing of 425 cancer-related genes. The plasma of a patient is defined as ctDNA positive only when one or more variants are detected in the plasma in at least 2% of primary tumors. All patients received standard nursing care.
The results showed that ctDNA could be detected in plasma of 38 patients before operation, but its value in predicting recurrence was limited. After operation, plasma ctDNA was still positive in 25 patients, and the risk of recurrence was higher than that in non positive patients. The plasma of 41 patients was evaluated after adjuvant chemotherapy. Among them, 10 patients with ctDNA positive had a significantly higher risk of recurrence and death than those with ctDNA negative.In particular, compared with postoperative ctDNA and tumor biomarkers after treatment, namely CEA, CA199 and CA72-4, ctDNA after adjuvant chemotherapy achieved better predictive performance, with a sensitivity of 77.8% and a specificity of 90.6%. CtDNA positivity was an independent factor for RFs in all multivariate analyses. Compared with ErbB4 wild-type patients, patients with ErbB4 mutations in primary tumors had poorer RFs. Therefore, after surgery and adjuvant chemotherapy, ctDNA is associated with residual lesions and high recurrence risk in patients with stage ii/iii gastric cancer, or can be used to guide the management of postoperative patients with gastric cancer.
3. Real world study: efficacy and safety of low-dose apatinib in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
Apatinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, which can inhibit the formation of tyrosine kinase by highly selective competition for the ATP binding site of VEGFR-2 in cells, thus inhibiting the formation of new blood vessels in tumor tissues, so as to achieve the purpose of anti-tumor. Studies have shown that apatinib has a good effect on advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, in the real world, the efficacy and safety of apatinib have yet to be studied. Therefore, this study aims to reveal the efficacy and safety of low-dose apatinib in the treatment of advanced HCC in the real world.
Between january2017 and August 2020, the researchers included 178 patients with advanced HCC who were treated with apatinib at three different institutions.
174 patients received 250 mg of oral apatinib per day and 4 patients received 500 mg per day until the disease progressed. Twenty five and 103 patients also received at least one immunotherapy and transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE), respectively. Tumor reaction and adverse reaction were evaluated according to RECIST 1.1 and CTCAE 5.0 respectively. The survival curve was analyzed using the Kaplan Meier method. Cox proportional hazards model was used to determine the prognostic value of univariate and multivariable.
The results showed that after 24 months of follow-up, patients achieved complete remission (CR), partial remission (PR), stable disease (SD) and progressive disease (PR) of 0 (0%), 28 (15.73%), 103 (57.87%) and 47 (26.40%) respectively. The overall remission rate (ORR) and disease control rate (DCR) were 15.73% and 73.60% respectively. Interestingly, among the 28 PR patients, 27 received apatinib as first-line or second-line therapy, and 21 received immunotherapy or TACE as combined therapy, indicating that early application of apatinib combined therapy can provide better efficacy.
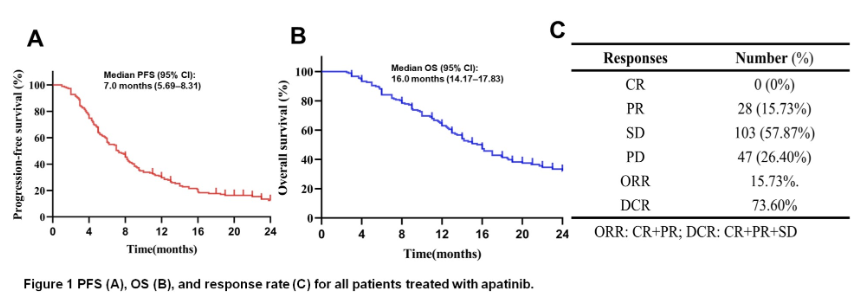
In addition, Kaplan Meier analysis showed that the median overall survival (OS) and progression free survival (PFS) were 16.0 months and 7.0 months, respectively. Third line therapy and PVTT were independently associated with poor PFS. In contrast, apatinib combined with immunotherapy, or independently associated with better PFS, also had better OS. In terms of adverse reactions, the most common treatment-related adverse events were hypertension (29.21%), fatigue (16.85%), hand foot syndrome (16.29%), vomiting (14.04%), liver dysfunction (6.18%) and proteinuria (6.74%). No serious (≥ grade 3) adverse events were observed.
In conclusion, low-dose apatinib can provide effective and safe treatment for advanced HCC, and early application of apatinib and combination therapy can provide better efficacy.
4. Comparison of four clinical prognostic scores in patients with advanced gastric cancer and esophageal cancer
Although there are several clinical scoring systems that can help to evaluate the prognosis of oncology clinical trials, there is no unified standard. This study compared the predictive ability of four prognostic scores for overall survival (OS) in patients with advanced gastric cancer and esophageal cancer (GE).
The study included patients with advanced (unresectable or metastatic) ge cancer who received first-line palliative system treatment from Princess Margaret cancer center in Canada from 2007 to 2020, and identified patients with high prognostic risk using four scoring systems. Royal Marsden Hospital score (RMH), MD Anderson Cancer Center score (MDACC), Gustave roussy immune score (grim-s) and MD Anderson immune checkpoint inhibitor (mda-ici) scores.
The results showed that a total of 451 patients with advanced Ge cancer were included. The median age was 59 years old, 68% were male, 51% had ECoG status of 0-1, and 63% showed new metastatic diseases. According to the four scores, the proportion of patients classified as high risk was RMH 25% (n=113), MDACC 13% (n=95), grim-s 24% (n=109), mda-ici 26% (n=117). In all scoring systems, the OS of high-risk patients was significantly shorter. (median OS 7.9 vs 12.2 months, RMH high risk vs low risk, p<0.001; MDACC 6.8 vs. 11.9 months, p<0.001; 5.3 vs. 13 months, p<0.001 for grim-s; 8.2 vs. 12.2 months, p<0.001 for mda-ici).
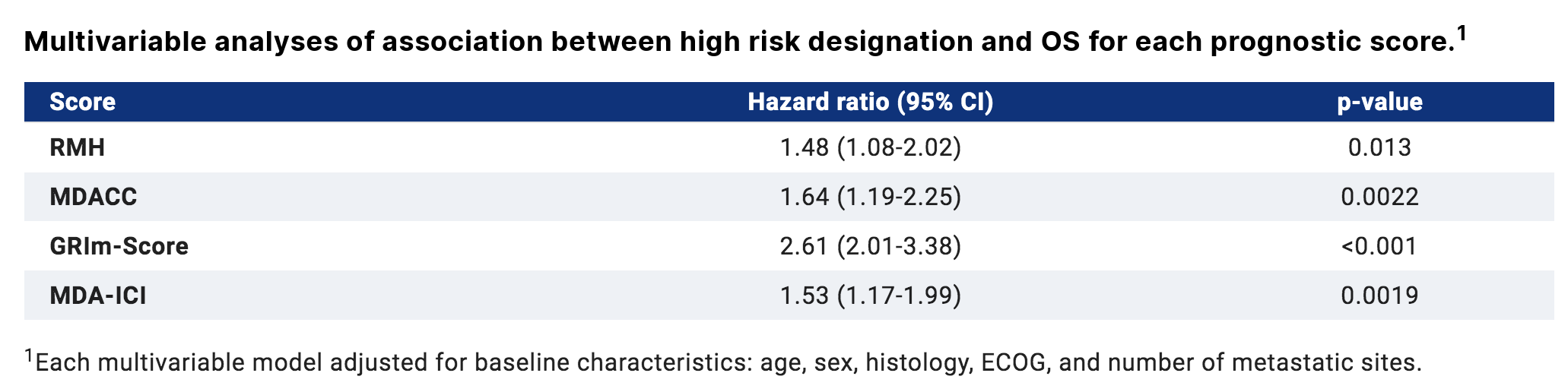
In multivariate analysis, each prognostic score was significantly associated with OS. Grim-s has the highest predictive discrimination and the highest predictive ability of early death.
In conclusion, the four prognostic scoring systems compared have reasonable accuracy in predicting OS in patients with advanced Ge cancer. The grim-s score may be preferred for higher accuracy in predicting early death.
Article source: