The WHO brain tumor classification system in 2016 and 2021 heralds an era of molecular pathology, enabling individual treatment and accurate prognostic stratification. Adult diffuse low-grade gliomas (LGG, histological grade 2-3) include a group of different genetic and biological entities, which seriously affect the quality of life (QOL) of patients. In short, the new classification system divides LGG into three independent subtypes, namely IDH 1/2 mutant 1p/19q co deletion oligodendrocytoma (idhmut codel), IDH 1/2 mutant 1p/19q non co deletion astrocytoma (idhmut noncodel) and IDH 1/2 wild-type glioma (now known as glioblastoma). Each entity has different responses to subsequent chemoradiotherapy, which requires accurate pre-treatment diagnosis for subsequent decision-making.

As we all know, the most safe resection of tumor is the basis of glioma treatment. Total resection (GTR) is always the ultimate and ideal goal to improve the survival rate. GTR is not always feasible, especially for tumors that invade expression regions or deep structures. Idhmut codel oligodendrogliomas usually show relatively inert tumor behavior and are associated with methylated MGMT promoter. Alkylating agent based chemotherapy can achieve satisfactory control of residual tumors. IDH wild-type gliomas have extremely aggressive, invasive and aggressive tumor behavior, so it is impossible to carry out radical surgical resection, and recurrence is inevitable. On the contrary, idhmut noncodel glioma patients can obtain considerable survival rate from GTR or even ultra total resection of tumors. Even very small residual tumors will have a great impact on the survival rate. Therefore, accurate and definite molecular diagnosis is very important for the subsequent operation planning.
Patel and other experts first reported that T2-FLAIR mismatch (t2fm) sign is a quite specific imaging biomarker of idhmut noncodel LGG, but its sensitivity is limited. T2fm refers to complete / near complete high signal on T2WI imaging, low signal on FLAIR sequence and high signal edge around. Some scholars have proposed that the sign that tumors show a single flair high signal edge (high flair edge) regardless of T2 performance is also a reliable indicator, which greatly increases the sensitivity of idhmut noncodel LGG.
Recently, a study published in the European Journal of Radiology combined the high flair margin and the imaging features in some reports to conduct a retrospective study in a large patient group to verify its practicability to clinicians, further improve the sensitivity of diagnosis of idhmut noncodel, and further guide the development of clinical personalized surgery.
This study retrospectively included consecutive adult patients with diffuse low-grade gliomas (LGG, histological grade 2-3) diagnosed between december1,2013 and december31,2020, and recorded and analyzed the clinical and radiological characteristics. According to the operation date, the patients were divided into queue a and queue B for training and verification (2:1).
A total of 585 patients were included in this study (cohort a, 390; cohort B, 195). When defining idhmut noncodel astrocytoma, high signal flair margin and low signal core (high flair margin) were more sensitive markers than T2-FLAIR mismatch (t2fm) (sensitivity in queue a: 0.713, 0.539, respectively; in queue B: 0.713, 0.489, respectively), but did not affect specificity (both 1.00). High flair margin, high rADC, homogeneous pattern on T2WI, non calcification and youth are the most important factors associated with idhmut noncodel astrocytoma. Combined with these factors, the stochastic forest model shows the best prediction ability.
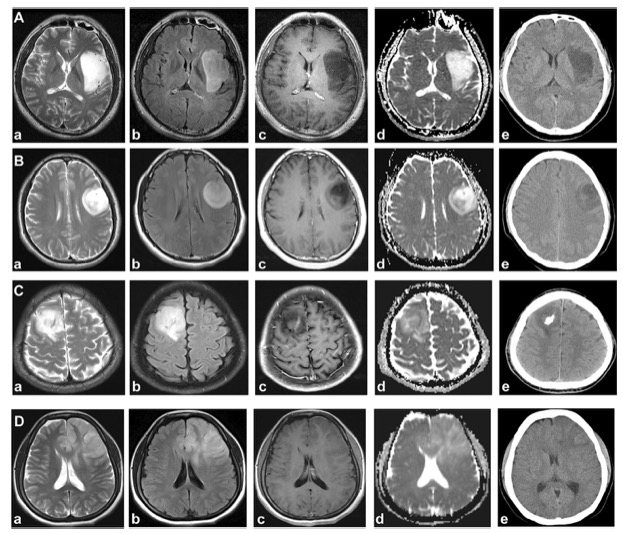
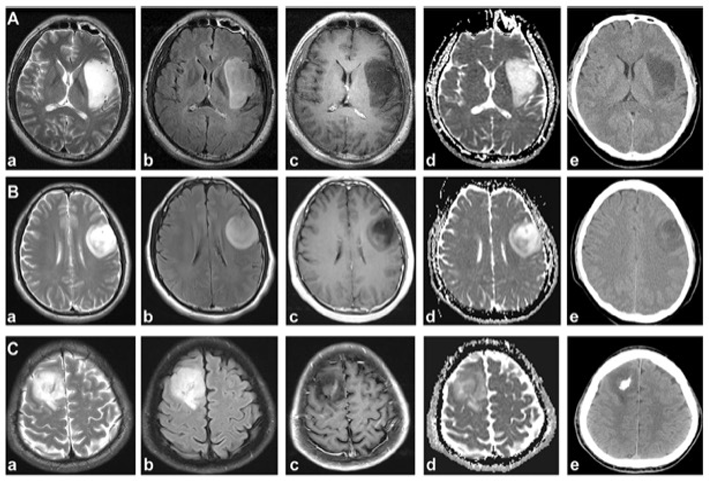
Figure representative examples of idhmut noncodel, idhmut codel and IDH wild-type gliomas. A. A typical example of idhmut noncodel and T2-FLAIR mismatch (t2fm). The patient showed uniform high signal (a) and high signal at flair edge on T2WI, but the core was low signal (high flair edge, (b), smooth edge (a, b), no enhancement (c), less diffusion restriction (d), and no calcification (E). B. Idhmut noncodel patients showed heterogeneous signal on T2WI (a), high flair margin and low signal core (b), no enhancement (c), and heterogeneous diffusion without calcification (E). Technically, due to the lack of uniform high signal on T2WI, this patient cannot be classified into t2fm subgroup, but this patient is idhmut noncodel astrocytoma. Thus, a single signal from the high flair margin is sufficient to diagnose this subgroup. C. Idhmut codel oligodendrocytomas often present heterogeneous signals on T2WI, with irregular margins (a), cortical involvement (c), mild enhancement (c), limited diffusion (d) and calcification (E). D. IDH wild-type glioma showed heterogeneous signals on MRI (A-D) and no calcification on CT (E)
This study shows that high flair margin is a sensitive and reliable imaging marker for the diagnosis of idhmut noncodel astrocytoma. Combined with high flair margin and other radiological features, idhmut noncodel astrocytoma can be accurately defined to guide clinical operation planning.
Original source:
Mingxiao Li,Xiaohui Ren,Xuzhu Chen,et al.Combining hyperintense FLAIR rim and radiological features in identifying IDH mutant 1p/19q non-codeleted lower-grade glioma. DOI:10.1007/s00330-021-08500-w
Article source:
https://www.medsci.cn/article/show_article.do?id=f3abe2858590