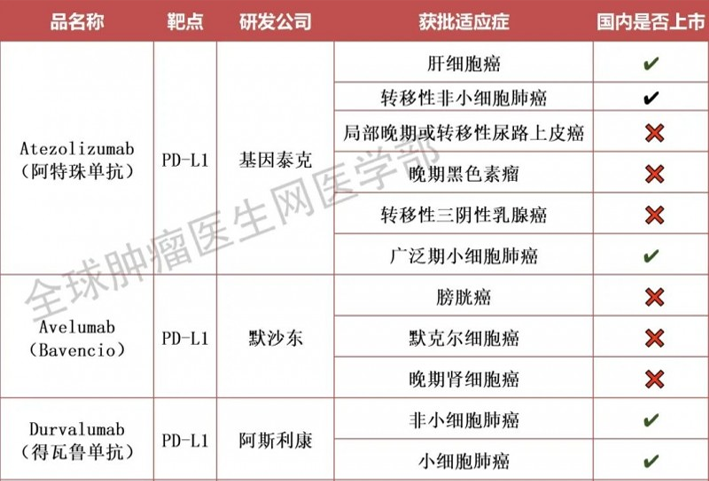
Sleep is a key determinant of health. Unhealthy sleep, such as short-term sleep deprivation, long-term sleep deprivation, circadian rhythm disorders, sleep disorders and excessive sleep, will have a far-reaching and adverse impact on physical health, mental health and mood, increasing the risk of a variety of chronic diseases and death, including Alzheimer's disease, anxiety, depression, cardiovascular disease, diabetes and obesity.
Sleep duration is becoming an important modifiable risk factor for cancer incidence rate and mortality. However, the specific relationship between sleep duration and cancer incidence rate and mortality is unclear. The purpose of this study was to explore the association between sleep duration and the risk of cancer onset and death.

Using data from six population-based cohorts, including 271694 participants, the researchers assessed the relationship between sleep duration and cancer incidence rate and mortality in Japanese adults. During a total follow-up of about 5.9 million person years, researchers found 40751 cancer cases and 18323 cancer deaths. The study specific risk ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated using Cox proportional hazards regression model, and the estimates were summarized using random effects meta-analysis.
The results showed that compared with sleep duration of 7 hours, sleep duration ≥ 10 hours was associated with a 19% increase in the risk of cancer incidence rate in women (HR 1.19, 95% CI 1.02-1.38), and the risk of cancer death in men (HR 1.18, 95% CI 1.00-1.39) and women (HR 1.44, 95% CI 1.20-1.73) increased by 18% and 44% respectively, but was not significantly associated with an increase in cancer incidence rate in men.
Compared with the sleep duration of 7 hours, the sleep duration of ≤ 5 hours has nothing to do with cancer incidence rate and mortality. However, in postmenopausal women, sleep duration of ≤ 5 hours and ≥ 10 hours were associated with an increased risk of cancer death compared with sleep duration of 7 hours.
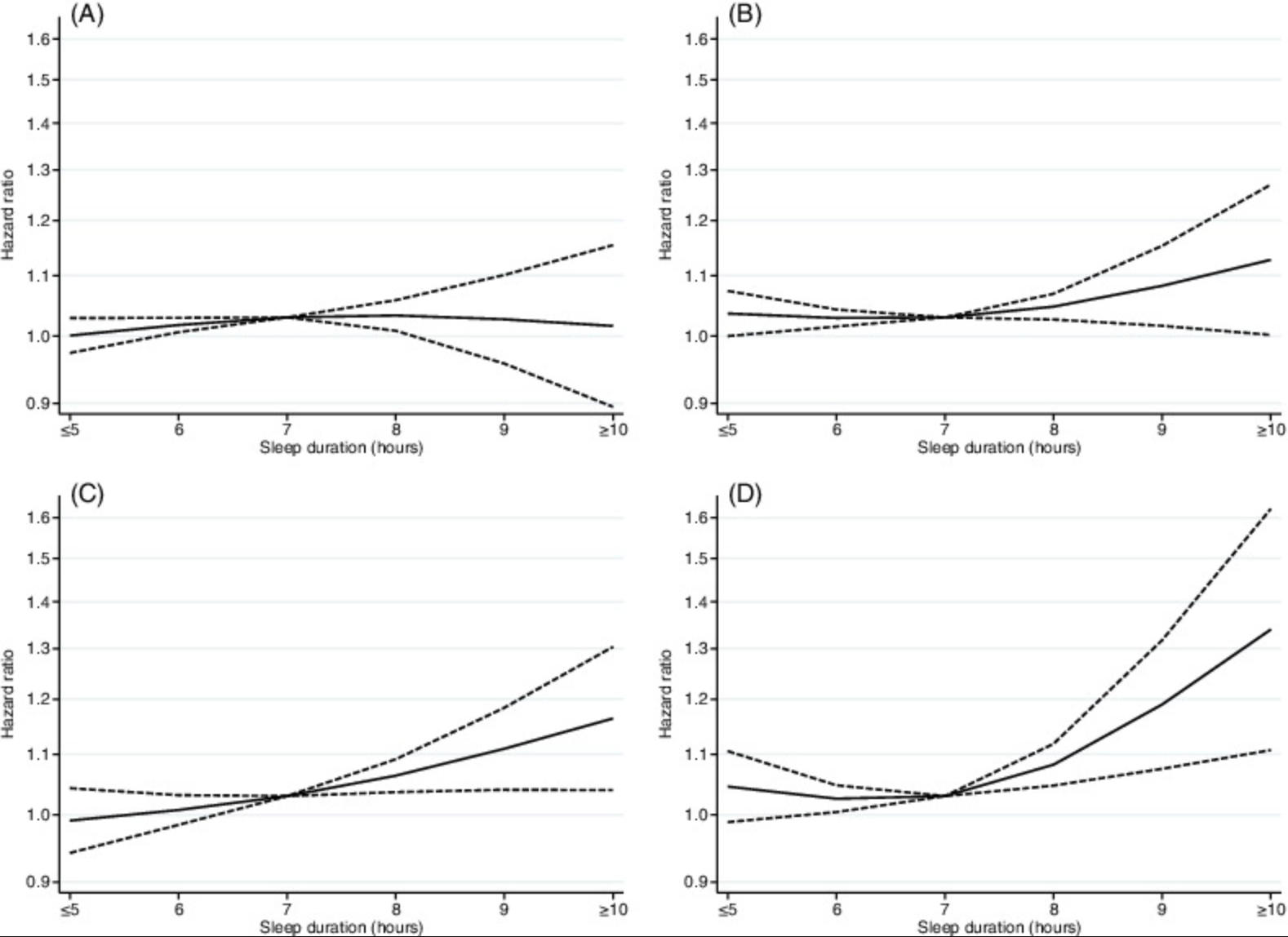
Overall, in this assessment of the data from the Japan cohort alliance, excessive sleep was associated with increased cancer mortality in men and women, and with increased cancer incidence rate in women. In postmenopausal women, both long and short sleep time are associated with increased cancer mortality. The results show that sleep duration is an important variable of cancer, which is of great significance for cancer prevention.
Source of original text:
Wilunda C, Abe SK, Svensson T, Sawada N, Tsugane S, Wada K, Nagata C, Kimura T, Tamakoshi A, Sugawara Y, Tsuji I, Ito H, Kitamura T, Sakata R, Mizoue T, Matsuo K, Tanaka K, Lin Y, Inoue M; Research Group for the Development and Evaluation of Cancer Prevention Strategies in Japan. Sleep duration and risk of cancer incidence and mortality: A pooled analysis of six population-based cohorts in Japan. Int J Cancer. 2022 May 26. doi: 10.1002/ijc. 34133. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35616624.
Reference link:
https://www.medsci.cn/article/show_article.do?id=1938e323475e