Immunotherapy is no stranger to cancer patients. In the past decade, immunotherapy has become one of the hottest fields in cancer research, fundamentally changing the treatment methods of many patients. It not only makes cancer patients see the hope of "cure", but also makes cancer treatment enter a new era.
Under the background of the increasingly popular immunotherapy in recent years, can we really look at its application value in tumor therapy objectively? How does this emerging technology help cancer patients improve their survival rate? In clinic, there are still many patients who know little about immunotherapy and do not know its indications, potential risks, timing and so on. The medical department of the global oncologist network will provide comprehensive and systematic science popularization for everyone, hoping to answer questions and help patients who want to choose immunotherapy.
1、 What is immunotherapy and how it works
Immunotherapy, also known as immunooncology, is a cancer treatment that enhances the body's natural defense against cancer. It uses substances made by the body or laboratory to improve or restore the function of the immune system, so as to use the power of the human body's own strong immune system to prevent, control and eliminate cancer.
On the one hand, the immune system can recognize and remove foreign invading bacteria and viruses. On the other hand, the immune system can also remove very small tumors in the body by itself. However, with the growth of age, immunity gradually declines. The occurrence of cancer is like a battle between cancer cells and the immune system in the body. In the end, the immune system is defeated. Cancer cells dominate the world, grow arbitrarily in the body and induce cancer. There are many reasons for the defeat of the immune system. In the final analysis, there are two:
1. Cancer cells camouflage well, making dendritic cells unable to recognize and kill cancer cells;
2. The number of immune cells in the body drops, and there is not enough force (killer T cells) to destroy cancer cells.
Immunotherapy can prevent or slow down the growth of cancer cells in the following ways.
● help train the immune system to better recognize and attack cancer cells.
● increase the number and attack power of immune cells to remove cancer cells.
● destroy cancer cells by releasing the "brake" mechanism of the immune system against cancer attacking molecules.
2、 What is the difference between immunotherapy and traditional drug therapy
Both targeted therapy and chemotherapy kill cancer cells directly through drug cytotoxicity, while immunotherapy kills cancer cells by activating immunity.
1: Different from targeted drugs, it has a broader spectrum of anticancer effects that do not distinguish the source of tumors (currently, the approved indications of immune checkpoint inhibitors have covered more than 20 kinds of blood and solid tumors, and adoptive cellular immunotherapy has also shown its effect on a variety of solid tumors in clinical studies).
2: Different from other treatments, its principle is to activate our own immune system to defeat cancer. Therefore, killing cancer cells accurately and avoiding attacks on normal cells are much smaller than the overall side effects of chemical drugs.
3: The immune system can adapt continuously and dynamically like cancer, so if the tumor tries to escape detection, the immune system can re evaluate and launch new attacks.
4: The immune system's "memory" enables it to remember what cancer cells look like, so it can target and eliminate cancer when it recurs.
5: If it takes effect, it may make late stage patients survive for a long time, or even cure clinically, which is the biggest difference between immunotherapy and all other drugs. Most patients who benefited from ipilimumab in the advanced melanoma trial are still alive today.
3、 What are the types of immunotherapy
What 90% of cancer patients do not know is that the immune therapy for cancer is not only the familiar pd-1/l1 or car-t. At present, immunotherapy is systematically divided into five categories: immunomodulator, monoclonal antibody, cancer vaccine, adoptive cell therapy and oncolytic virus.
01. Immunomodulators: checkpoint inhibitors, cytokines, agonists and adjuvants
Immunomodulators are molecules that act on pathways that regulate the activity of the immune system. With more and more understanding of the braking and accelerator mechanisms of the immune system, the medical community has developed a large number of therapies for these two immune mechanisms to improve the ability of the immune system to attack and eliminate cancer. One of the most successful is the immune checkpoint inhibitor.
01. immune checkpoint inhibitor
PD-1 / PD-L1, CTLA-4, LAG-3 pathways are critical to the ability of the immune system to control cancer growth. These pathways are often referred to as immune checkpoints. Many cancers use these pathways to escape the immune system. Specific antibodies to immune checkpoint inhibitors can block these pathways in response to cancer. Once the immune system can detect and respond to cancer, it can prevent or slow the development of cancer. For example, the pd-1/pd-l1 immune checkpoint pathway can shut down T cells that target cancer.
However, when checkpoint inhibitors block the pd-1/pd-l1 pathway, they enable T cells to eliminate cancer cells.
By 2022, 9 kinds of immune checkpoint inhibitors have been listed in dozens of European and American countries.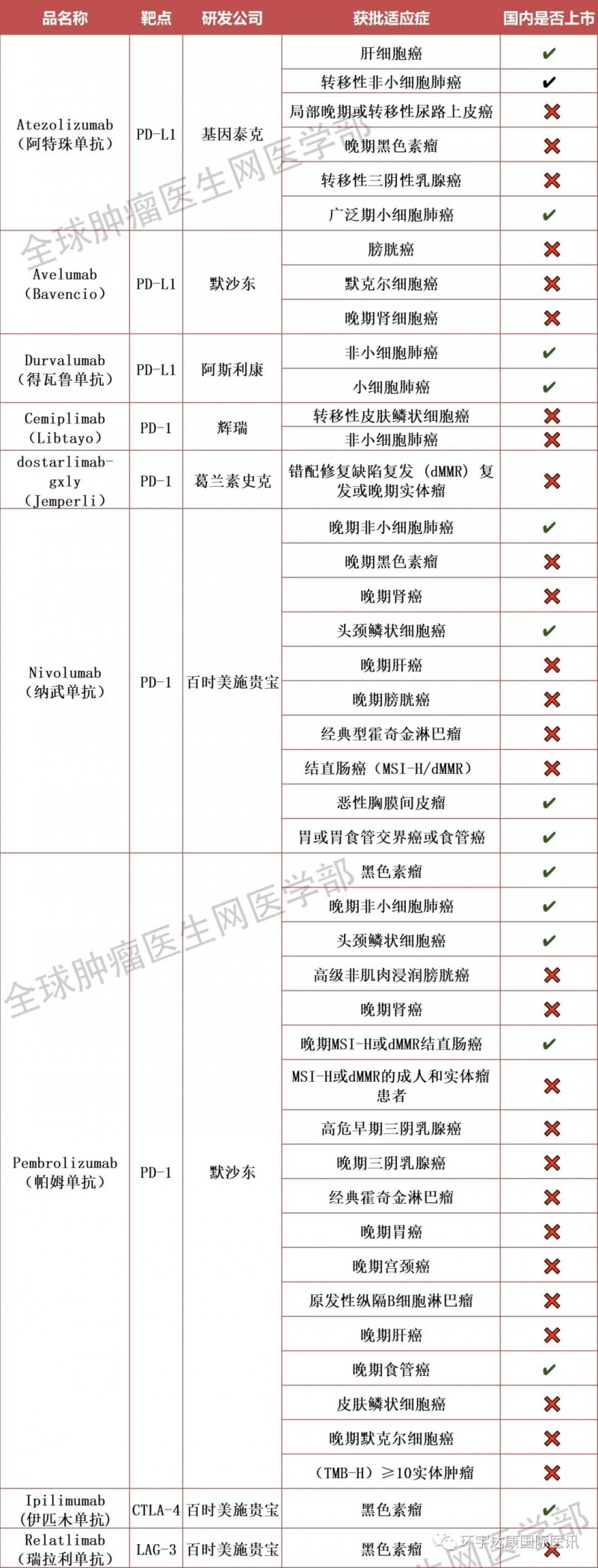
9 immune checkpoint inhibitors listed in Europe and America
02. cytokines
Cytokines are messenger molecules that regulate the maturation, growth and reactivity of immune cells. This nonspecific immunotherapy also helps the immune system destroy cancer cells. Most nonspecific immunotherapies are given after radiotherapy and chemotherapy or at the same time. Currently, there are four FDA approved cytokine immunotherapies for patients with renal cell carcinoma, leukemia, lymphoma, melanoma and sarcoma.
●Aldesleukin (Proleukin ®): A cytokine that targets the il-2/il-2r pathway; Approved for subset of patients with renal cancer and melanoma
● granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF): an immunomodulatory cytokine; Approved for use in a subgroup of patients with neuroblastoma
● interferon alfa-2a: a cytokine targeting the ifnar1/2 pathway; Subgroup approved for leukemia and sarcoma patients
● interferon alfa-2b (intron a ®): A cytokine targeting the ifnar1/2 pathway; Approved for use in subpopulations of patients with leukemia, lymphoma, melanoma, and sarcoma
●Peginterferon alfa-2b (Sylatron ®/ PEG-Intron ®): A cytokine targeting the IFNAR1 pathway; Approved for melanoma patient subpopulation
03. agonists
Agonists activate pathways that promote adaptive immune response by helping to activate "killer" T cells that directly attack cancer cells or stimulating the activity of innate immune cells (such as dendritic cells), which coordinate the overall immune response against cancer and enhance T cell activity by expressing cancer markers.
04. adjuvant
Adjuvants can activate the innate immune system, stimulate the general immune response and ultimately promote the adaptive immune response. FDA approved adjuvant immunotherapy is currently available to treat a subset of patients with squamous cell carcinoma, a skin cancer.
● imiquimod: an immune adjuvant targeting toll like receptor 7 (TLR7) pathway; Approved for subgroup of patients with basal cell carcinoma
●Poly ICLC (Hiltonol ®): An immune adjuvant targeting toll like receptor 3 (TLR3) pathway; Approved for use in a subset of patients with squamous cell carcinoma
02. Adoptive cellular immunotherapy
Adoptive immune cell therapy technology is to collect human autoimmune cells, culture them in vitro, increase their number by a thousand times, enhance the targeted killing function, and then transfuse them back into the patient's body, so as to kill pathogens, cancer cells and mutant cells in the blood and tissues.
The 7 approved car-t therapies in the world have brought subversive survival benefits to patients with blood tumors; In addition, in January, 2022, kimmtrak, the world's first tcr-t therapy for solid tumors, was also approved, which means that T-cell therapy formally challenges solid tumors and is a milestone! Recently, we have received good news again. TILs therapy, which has attracted much attention in the field of solid tumors, has received positive feedback from FDA. It is planned to formally submit the listing application before August 2022, which means that the famous TILs therapy is getting closer and closer to being officially approved for listing!
In addition, many immunotherapies are conducting clinical trials on a variety of cancer types. More and more immunotherapies are emerging to challenge cancer and bring unprecedented survival breakthroughs to cancer patients!
01.CAR-T
Car-t treatment is to transform the patient's immune cells, introduce the receptor gene that can encode and recognize tumor specific antigen and various gene fragments that help T cells activate, and form car-t cells. These cells not only carry the "navigation head" for tumor recognition, but also enhance the "ammunition depot" for self killing tumor. After in vitro expansion and culture, the transformed T cells are reinfused into the patient, Once the tumor cells expressing the corresponding antigens are met, they will be activated and re expanded to exert their great specific lethality and kill the tumor.
At present, FDA has approved six car-t therapies, two car-t products have been launched in China, and seven car-t therapies have been approved worldwide!
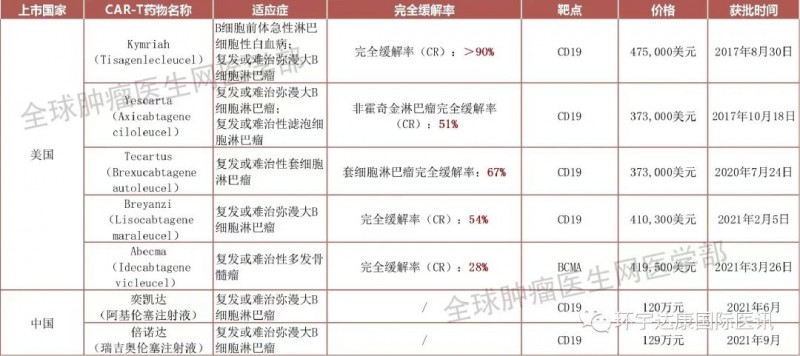
Approved car-t therapy
02.TCR-T
Tcr-t technology, namely T cell receptor (TCR) chimeric T cell technology, is also called affinity enhanced TCR "technology. Its purpose is to make its killer T cells have stronger recognition ability. Because the original T cells have weak recognition ability to tumor related antigens, now they can enhance the recognition affinity through gene modification, so that T cells can attack tumor cells and achieve the effect of tumor treatment.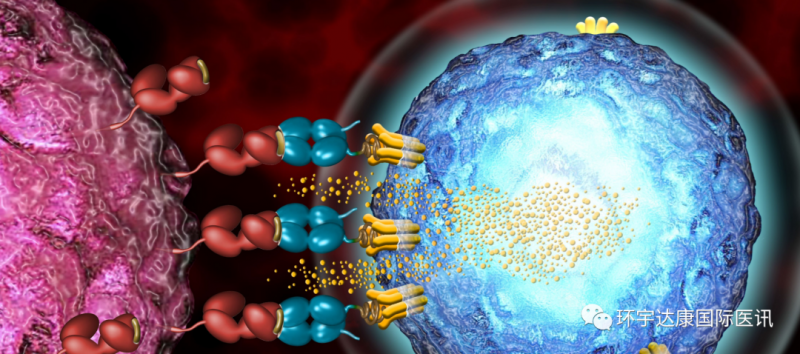
Tcr-t cell
In January, 2022, the FDA approved tebentafusp tebn (kimmtrak, immunocore Limited), a bispecific gp100 peptide HLA directed CD3 T cell conjugator for hla-a*02:01 positive unresectable or metastatic uveal melanoma. This is the world's first approved tcr-t therapy for solid tumors, which means that T cell therapy formally challenges solid tumors and is of milestone significance!
03.TILs
Til therapy is a method to isolate til cells from the tissues near the tumor, add growth factor IL-2 for massive expansion in vitro, and then transfuse them back into the patient's body, so as to expand the immune response and treat primary or secondary tumors. This therapy uses T cells that can identify and target patients' tumors as an immune force to overcome cancer. It is an individualized anti-cancer therapy tailored to each cancer patient. It has the characteristics of polyclonal, specific recognition of a variety of new antigens, individualization, high specificity, durability, and immune memory after infusion.
Recently, TILs therapy ln-144 (lifileucel), which has attracted much attention in the field of solid tumors, has received positive feedback from FDA. It is planned to formally submit the listing application before August 2022. Once approved, it will be the first one-time cell therapy for solid tumors. In addition, gt101, the first til cell drug in China, has also been approved by the China food and drug administration to officially carry out clinical trials, which means that the well-known TILs therapy is getting closer and closer to being officially approved for listing!
04.CAR-NK
NK cells are the first line of defense of the immune system. The situation feedback is timely. Once the "enemy situation" is found, it is quickly "reported" and the immune defense and immune killing functions of the entire immune system are activated. Unlike T cells, they directly detect and destroy infected and malignant cells without being activated or "trained" to respond to cancer cells. Therefore, it is one of the ideal cell therapies integrating efficacy, safety and relative ease of use.
The success of car-t cell therapy has stimulated people's enthusiasm for using car gene to modify NK cells to enhance their tumor killing ability. This idea is similar to the construction of car-t: a chimeric antibody car (including extracellular recognition domain (such as scFv)) that can recognize tumor cells and activate NK cells to kill tumor cells is added to NK cells by genetic engineering to recognize tumor specific antigens; A transmembrane domain and an intracellular signal domain (CD3 ζ Chain) can induce the activation of NK cells), which means that NK cells are equipped with a "GPS navigation" system to kill tumor cells accurately and efficiently in vivo. At present, car-nk therapy has blossomed everywhere in blood and solid tumors and made many breakthroughs.
03. Cancer vaccine
For decades, cancer vaccine has become a form of immunotherapy, which promotes the immune system to attack cancer cells carrying tumor specific or tumor related antigens by triggering immune responses. Cancer vaccines can be made from a variety of components, including cells, proteins, DNA, viruses, bacteria and small molecules, to produce immune stimulating molecules. These include preventive and therapeutic cancer vaccines.
Preventive cancer vaccine: HPV vaccine is the most well-known cancer preventive vaccine. It can prevent human papillomavirus infection. It has been confirmed that some HPV infections are associated with cervical cancer, vaginal cancer, vulvar cancer, penile cancer, anal cancer, rectal cancer and head and neck cancer.
Therapeutic cancer vaccine: as for the therapeutic cancer vaccine, Provenge (sipuleucel-t), the first and only one approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in the world, has realized the idea of attacking cancer cells by using the patient's own immune system for the first time. This approval marks the success of 20 years' unremitting efforts.
Product name Provenge
Company name American denreon company
Preparation method unknown
purpose cancer vaccine
Price $93000
In the past two years, the research and development of global cancer vaccines have blossomed everywhere, and exciting research data have been obtained in various cancers. The medical department of the global oncologist network has consulted a large number of literatures, and selected some cancer vaccine frontier research with heavy data for all kinds of cancers, which is expected to be on the market, hoping to give patients more hope and confidence in overcoming cancer!
04. Oncolytic virus
Oncolytic virus is a kind of virus that can effectively infect and destroy cancer cells. Due to the characteristics of the virus, this therapy can be applied systematically or locally to treat primary and metastatic tumors. When the cancer cells break and die under the infection of virus, the newly generated virus particles will be released to further infect the surrounding cancer cells. In terms of mechanism, it can not only kill tumors directly, but also stimulate the immune response of human body and enhance the anti-tumor effect.
In 2015, the US Food and Drug Administration approved the first oncolytic viral therapy for melanoma. The virus used in treatment is called talimogene laherparepvec (imlygic) or t-vec. The virus is a genetically modified version of herpes simplex virus and can cause herpes labialis. Doctors can inject t-vec directly into melanoma areas that cannot be removed by surgeons. At present, t-vec has been widely used in the treatment of recurrent melanoma in the United States, Europe and Australia. On June 11, 2021, the world's first oncolytic viral therapy for the treatment of primary brain tumors was approved in Japan. Patients who want to know can call the medical department for details. In addition, oncolytic viruses have also made great breakthroughs in other solid tumors:
1. A small study published at the 2019 AACR annual meeting showed that most patients with triple negative breast cancer achieved pathological complete remission (PCR) after receiving t-vec (imlygic) and neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Triple negative breast cancer
2. Nx-2401 is a novel oncolytic adenovirus targeting brain tumors. It has tumor selectivity, enhanced infectivity and strong replication ability. To assess the safety and efficacy and to determine the biological effects of increasing viral doses, 37 patients with recurrent gliomas, including glioblastoma (89%), gliosarcoma (5%), and anaplastic astrocytoma (5%), were recruited.
For patients with recurrent glioblastoma with a median survival of 6 months, dnx-2401 can help 20% of them survive for more than 3 years. Among the five long-term survivors, three more achieved lasting remission.
At present, the vaccine is undergoing phase II clinical trial (nct02798406) in famous cancer centers such as MD Anderson and memorial Sloan in the United States
Oncolytic virus
05. Targeted antibody
CRI (American Cancer Institute) classifies targeted antibody as a kind of cancer immunotherapy, which can destroy the activity of cancer cells and remind the immune system to target and eliminate cancer cells.
Antibodies are proteins naturally produced by immune cells called B cells that protect us from threats such as bacteria, viruses, and cancer cells. Antibodies do this by precisely targeting and binding to cell surface markers called antigens. On its own, our immune system is capable of producing trillions of different types of antibodies. Now, scientists can complement our immune system by creating and customizing antibodies against specific cancer targets in the laboratory. At present, it is mainly divided into the following three categories:
● "naked" monoclonal antibody (mAb). Such as bevacizumab and cetuximab
● antibody drug conjugate (ADC). For example: trodelvy, enhertu ®
● bispecific antibody. For example: rybrevant, kimmtrak ®
4、 What are the current FDA approved immunotherapies
As of march2022, the US Food and drug administration has approved a total of 60 immunotherapies, which cover almost all major cancer types (A-Z order):
1. Aldesleukin (immunomodulator) in the treatment of renal cell carcinoma and melanoma
2. alemtuzumab (targeted antibody) in the treatment of leukemia
3. Amivantamab (bispecific antibody) in the treatment of lung cancer
4. Atezolizumab (checkpoint inhibitor) for bladder cancer, liver cancer, lung cancer and melanoma
5. Avelumab (checkpoint inhibitor) for the treatment of bladder cancer, kidney cancer and skin cancer (Merkel cell carcinoma)
6. Axicabtagene ciloleucel (car T cell therapy) for lymphoma
7. Bacillus Calmette Gu é Rin [bcg] (vaccine) in the treatment of bladder cancer
8. Belantamab mafodotin blmf (antibody drug conjugate) in the treatment of multiple myeloma
9. bevacizumab (targeted antibody) for brain cancer, cervical cancer, colorectal cancer, kidney cancer, liver cancer, lung cancer and ovarian cancer
10. blinatumomab (bispecific T cell binding antibody) for leukemia
11. Brentuximab vedotin (antibody drug conjugate) in the treatment of lymphoma
12. Brexucabtagene autoleucel (car T cell therapy) for leukemia and lymphoma
13. Cemiplimab (checkpoint inhibitor) for lung cancer and skin cancer (basal cell carcinoma and skin squamous cell carcinoma)
14. cetuximab (targeted antibody) for colorectal cancer and head and neck cancer
15. Treatment of multiple myeloma with ciltacabtagene autoleucel (car T cell therapy)
16. daretouximab (targeted antibody) for multiple myeloma
17. dinomab (targeted antibody) in the treatment of sarcoma
18. Dinutuximab (targeted antibody) for neuroblastoma in children
19. Dostarlimab (checkpoint inhibitor) for uterine (endometrial) cancer
20. Treatment of lung cancer with durvalumab (checkpoint inhibitor)
21. Elotuzumab (targeted antibody) in the treatment of multiple myeloma
22. Enfortumab vedotin ejfv (antibody drug conjugate) in the treatment of bladder cancer
23. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin (antibody drug conjugate) in the treatment of leukemia
24. granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor or GM-CSF (immunomodulator) for neuroblastoma
25. hepatitis B vaccine (recombinant) (preventive vaccine) for liver cancer
26. human papillomavirus tetravalent (types 6, 11, 16 and 18) vaccine, used for recombination of cervical cancer, vulvar cancer, vaginal cancer and anal cancer (preventive vaccine)
27. human papillomavirus 9-valent vaccine for recombination of cervical cancer, vulvar cancer, vaginal cancer, anal cancer and laryngeal cancer (preventive vaccine)
28. human papillomavirus bivalent (types 16 and 18) vaccine for recombinant cervical cancer (preventive vaccine)
29. Ibritumomab tiuxetan (antibody drug conjugate) in the treatment of lymphoma
30. Treatment of multiple myeloma with ideabtagene vicleucel (car T cell therapy)
31. imiquimod (immunomodulator) for skin cancer (basal cell carcinoma)
32.inotuzumab ozogamicin (antibody drug conjugate) in the treatment of leukemia
33. interferon alfa-2a (immunomodulator) for leukemia and sarcoma
34. interferon alfa-2b (immunomodulator) for leukemia, lymphoma and melanoma
35. Ipilimumab (checkpoint inhibitor) is used for colorectal cancer, liver cancer and lung cancer, as well as melanoma and mesothelioma
36. Isatuximab (targeting any antibody) in the treatment of multiple myeloma
37. Lisocabtagene maraleucel (car T cell therapy) for lymphoma
38. loncastuximab tesirine (antibody drug conjugate) for lymphoma
39. Margetuximab (targeted antibody) for breast cancer
40. Treatment of lymphoma with mogamulizumab (targeted antibody)
41. Naxitamab gqgk (targeted antibody) for neuroblastoma
42. Treatment of lung cancer with necitumumab (targeted antibody)
43. Nivolumab (checkpoint inhibitor) is used for bladder cancer, colorectal cancer, esophageal cancer, GEJ, head and neck cancer, renal cancer, liver cancer, lung cancer and gastric cancer, lymphoma, melanoma and mesothelioma
44. Obinutuzumab (targeted antibody) in the treatment of leukemia and lymphoma
45. Treatment of leukemia with ofatumumab (targeted antibody)
46. panimab (targeted antibody) in the treatment of colorectal cancer
47. pegylated interferon alfa-2b (immunomodulator) in the treatment of melanoma
48. Pembrolizumab (checkpoint inhibitor) is used for bladder cancer cancer, breast cancer, cervical cancer, colorectal cancer, esophageal cancer, head and neck cancer, renal cancer, liver cancer, gastric cancer, lung cancer and uterine cancer, as well as lymphoma, melanoma and any MSI-H or tmb-h solid cancer, regardless of origin
49. pertuzumab (targeted antibody) in the treatment of breast cancer
50. Pexidartinib (immunomodulator) for giant cell tumor of tendon sheath
51. Polatuzumab vedotin (antibody drug conjugate) in the treatment of lymphoma
52. poly ICLC (immunomodulator) for skin cancer (squamous cell carcinoma)
53. Ramucirumab (targeted antibody) is used for colorectal cancer, esophageal cancer, liver cancer, lung cancer and gastric cancer
54.relatlimab (checkpoint inhibitor) in the treatment of melanoma
55. rituximab (targeted antibody) for leukemia and lymphoma
56. Sacituzumab govitecan hziy (antibody drug conjugate) for bladder cancer and breast cancer
57. sipuleucel-t (vaccine) for prostate cancer
58. tafasimab (targeted antibody) for lymphoma
59. tebentafusp tebn (bispecific antibody) of melanoma
60. Tisagenlecleucel (car T cell therapy) for leukemia (including children) and lymphoma
61. tisotumab vedotin (antibody drug conjugate) for cervical cancer
62. trastuzumab (targeted antibody) for breast cancer, esophageal cancer and gastric cancer
63. trastuzumab deruxtecan (antibody drug conjugate) for breast cancer, esophageal cancer and gastric cancer
64. trastuzumab emtansine (antibody drug conjugate) for breast cancer
65. t-vec of melanoma (oncolytic virus)
At present, many new immunotherapies are being developed to cover almost all types of cancer.
5、 Which cancer patients receive immunotherapy
The popularity of immunotherapy still cannot be compared with surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy. However, immunotherapy has been approved to treat a variety of cancers. There are more than 20 kinds of cancers that can be treated with immunotherapy, among which the earliest are melanoma, renal cancer, sarcoma, and solid tumors, such as lung cancer, gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, etc.
Immunotherapy is becoming more and more broad-spectrum, with mild toxic and side effects. However, in the process of immunotherapy, patients must be screened, and the indications and contraindications of immunotherapy must be strictly mastered. Once the side effects of immunotherapy appear, they are likely to be fatal. For example, changes in lung stroma, interstitial pneumonia, myocardial damage, etc., will increase the mortality of patients. During the whole treatment process, the doctor will control the indications and toxic and side effects, and make timely communication with the patients and their families during the treatment process.
The prospect of immunotherapy is very good. With the deepening of clinical research, immunotherapy may have new breakthroughs in various solid tumors.
6、 How to judge whether immunotherapy is effective
Compared with traditional therapy, immunotherapy may take longer to produce detectable signs of tumor shrinkage. Sometimes the tumor may grow even before it becomes smaller, because with the infiltration of immune cells and the invasion of cancer cells, the tumor will expand. This phenomenon, known as pseudoprogression, occurs only in immunotherapy. In some cancer types, immune related side effects predict treatment success, especially in melanoma patients with vitiligo (spotted skin loss) - but for the vast majority of patients, there is no clear link between side effects and treatment effects.
7、 What are the limitations of immunotherapy
Immunotherapy has a lot of promise as a cancer treatment. However, it may cause some problems. The reaction may be bad. Areas of the body where the drug enters may be injured, itchy, swollen, red or painful. There are side effects. Some types of immunotherapy will speed up the immune system and make you feel like you have the flu, accompanied by fever, chills and fatigue. Others may cause swelling, weight gain, palpitations and diarrhea.
Most of the time, these are relieved after the first treatment. It can damage organs and systems. Some of these drugs can cause your immune system to attack organs such as the heart, liver, lungs, kidneys or intestines. It doesn't work quickly. In some cases, immunotherapy takes longer to respond than other therapies. So cancer won't go away soon.
8、 What are the side effects of immunotherapy
Immunotherapy may cause side effects. The most common side effects are skin reactions at the injection site: swelling, pain, redness, itching, rash
You may have flu like symptoms, including fever, chills, weakness, dizziness, nausea or vomiting, muscle or joint pain, fatigue, headache, dyspnea, hypotension or hypertension
Other side effects may include: palpitations, sinus congestion, diarrhea, infection risk, organ inflammation
9、 What are the biomarkers of immunotherapy
Like targeted therapy, immunotherapy also needs to find cancer specific biomarkers to accurately attack the unique characteristics of cancer cells. Some substances produced and released by tumor cells often exist in tumor cells or host body fluids in the form of antigens, enzymes, hormones and other metabolites. Tumors can be identified according to their immune characteristics.
At present, biomarkers related to the efficacy of immunotherapy are mainly classified as follows:
Tumor antigen: MSI-H / dmmr, neoantigen, TMB
Inflammatory tumor markers: inflammatory genes, PD-L1, PD-L2, tumor infiltrating lymphocytes
Immunosuppressive markers: ido1, LAG-3, MDSC, regulatory T cells
Intestinal microorganism
10、 What are the acceptable immunotherapies for cancer patients in China
In the past, it took at least 3-5 years for anti-cancer drugs to enter China. In the past two years, with the attention of the government, China has accelerated the pace of anti-cancer drugs entering the market. At present, a variety of immunotherapies with significant anti-cancer effects in the United States have been listed in China, bringing more choices and hopes to Chinese cancer patients.
Overview of PD-1 inhibitors listed in China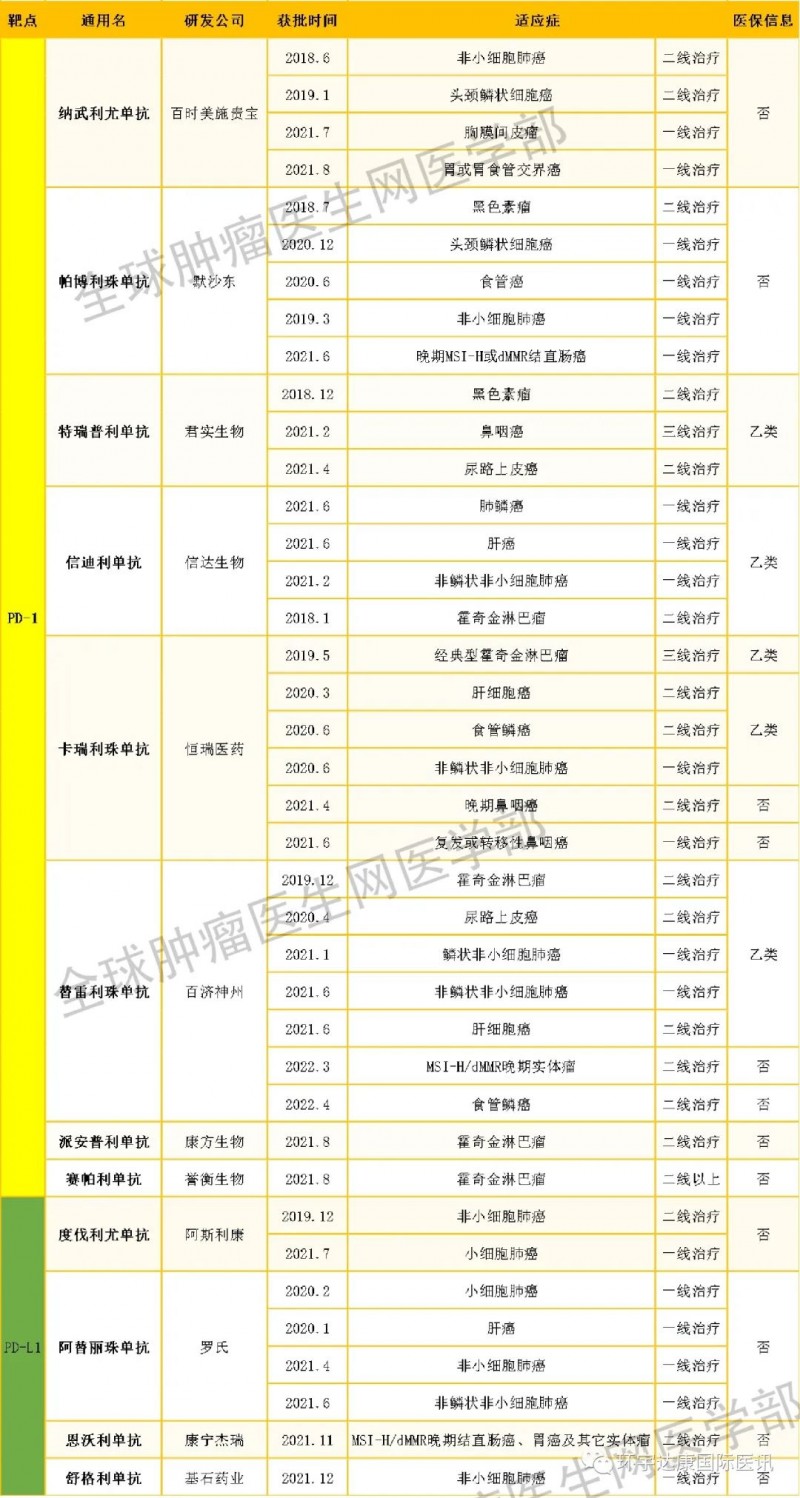
In addition to immune checkpoint inhibitors, in recent years, cell therapy has brought new hope to patients with refractory diseases such as malignant tumors, some infectious diseases and genetic diseases, and has begun to enter clinical application in developed economies such as the United States, Europe and Japan in a variety of ways. Medical institutions in China have also carried out a large number of clinical studies, and the voice of patients who want to receive high-quality cell therapy is increasing. The government is also standardizing and accelerating the scientific development of cell therapy, and allowing somatic cell therapy projects that have been proved to be safe and effective by clinical research to enter the transformation application in relevant medical institutions after filing. Relevant clinical trials are also being carried out.
At the same time, it is necessary to remind the patients that the treatment of tumor must rely on the regular treatment of authoritative hospitals and experts. After taking the conventional treatment methods (surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy) and according to their own economic conditions, the comprehensive therapy such as adjuvant immunotherapy technology can achieve the purpose of sclerotherapy, prevent recurrence, improve life treatment, and prolong the survival period, and finally achieve the success of anti-cancer. If you want to fully understand your immune status or related immunotherapy, please call the medical department or join the immunotherapy doctor-patient exchange group.
Reference material:
https://blog.dana-farber.org/insight/2019/07/immunotherapy-what-it-is-how-it-works-and-current-research/_ga=2.85278873.1806986239.1563027216-391867544.1549545797
https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/types/immunotherapy
https://www.cancerresearch.org/immunotherapy/what-is-immunotherap
Article source:
http://www.globecancer.com/azzx/show.php?itemid=15135