Introduction: in the case of early detection of breast cancer, patients usually get better treatment results. However, once the cancer starts to metastasize, the difficulty of treatment will greatly increase. So far, the research on cancer has paid little attention to the problem of when tumors shed metastatic cells. Recently, scientists have made an amazing discovery: when patients sleep, the metastasis and spread of breast cancer accelerate.
According to the data of the World Health Organization (who), breast cancer is one of the most common cancers, with about 2.3 million new breast cancer patients every year. If breast cancer can be detected early, patients will usually get good treatment results. However, once the cancer starts to metastasize, the difficulty of treatment will greatly increase. When circulating cancer cells (CTC) break away from the original tumor, spread through blood vessels in the body and form new tumors in other organs, cancer metastasis occurs.
So far, the research on cancer has paid little attention to the problem of when tumors shed metastatic cells. The researchers previously thought that tumors release these cells continuously. However, a new study conducted by researchers from ETH Zurich, University Hospital Basel and University of Basel has come to a striking conclusion: most of the circulating cancer cells that produce metastasis appear during the sleep of patients. The results of the study were published in nature.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-04875-y
Higher levels of circulating cancer cells during sleep
Nicola Aceto, the study leader and professor of molecular oncology at the Federal Institute of technology in Zurich, concluded: "when the patient falls asleep, the tumor will wake up."
The researchers analyzed a sample of 30 female cancer patients. These female patients were in a state of untreated or suspended treatment. The research team collected their blood samples at 10 a.m. (awake) and 4 a.m. (asleep). They found that when patients went to sleep, tumors produced more circulating cells. Compared with the circulating cells shed from the tumor during the day, the cells shed at night divide faster, so they are more likely to form metastasis.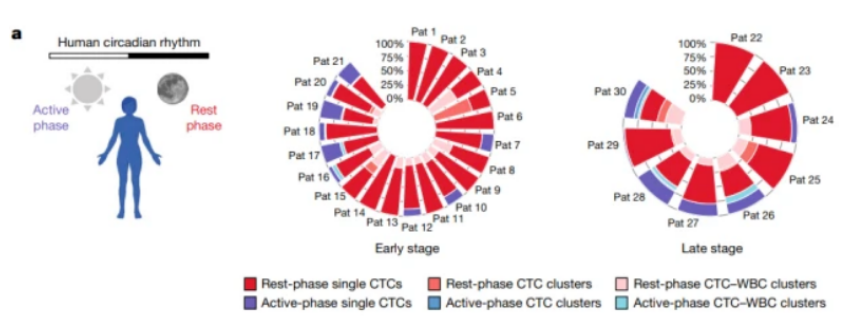
After finding this, researchers believe that circadian rhythm may affect the process of cancer metastasis. So the team designed a group of tumor mouse models of breast cancer and began to conduct deeper analysis.
The results of the samples from mice and human patients are just the opposite: the level of circulating cancer cells during the day is higher than that at night. The reason behind this is that, as a nocturnal animal, mice sleep during the day and move at night. Therefore, the essence of the experimental results is that more circulating cells fall off at night. Later, the researchers disrupted the mice's rhythms, confusing their rest and activity time. After a period of time, it was found that the circulating cancer cells of mice still increased at rest and decreased during activity.
Circadian rhythm regulating hormone controlling metastasis
If circadian rhythms affect cancer metastasis, is it related to hormones that affect circadian rhythms?
The team artificially increased melatonin in mice. They observed that melatonin significantly increased the number of circulating cancer cells in the blood of mice. When melatonin receptor inhibitors were added, circulating cancer cells in the blood decreased.
ZOI diamantopoulou, the lead author of the study and a postdoctoral researcher at the Federal Institute of technology in Zurich, said: "our study shows that the shedding of circulating cancer cells from primary tumors is controlled by hormones such as melatonin, which determine our circadian rhythm."
Adjust treatment
The results also reflect that the time taken to diagnose tumors or blood samples may affect the analysis of oncologists. Aceto smiled and said, "some of my colleagues usually work in the morning or evening, but sometimes they also analyze blood at other times." Scientists were surprised to find that the level of circulating cancer cells varied greatly in samples collected at different times of the day.
"In our view, health care professionals may need to systematically record when they perform biopsies on patients, which will help to make the data truly comparable," Aceto said
Next, researchers will think about how to integrate these findings into existing cancer treatments to optimize treatment. In addition, as a further study, Nicola Aceto wants to study whether different types of cancer are similar to breast cancer, and whether existing therapies will be more effective if patients receive treatment at different times.
Reference material:
Diamantopoulou Z, Castro-Giner F, Schwab FD, Foerster C, Saini M, Budinjas S, Strittmatter K, Krol I, Seifert B, Heinzelmann-Schwarz V, Kurzeder C, Rochlitz C, Vetter M, Weber WP, Aceto N.The metastatic spread of breast cancer accelerates during sleep. Nature. 2022 Jun 22. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04875-y
https://medicalxpress.com/news/2022-06-breast-cancer-night.html
Source link:
https://www.medsci.cn/article/show_article.do?id=249ce3040447