Inflammation and insulin resistance (IR) play an important role in various chronic diseases, including cancer. Cancer remains the leading cause of death worldwide. According to the global cancer statistics 2020, it is estimated that there are 19.3 million new cancer diagnoses and 10million cancer-related deaths in 2020. In many studies, markers of systemic inflammation have been associated with increased cancer risk and mortality, including esophageal cancer, gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, liver cancer, pancreatic cancer, bladder cancer, and lung cancer. Epidemiological studies have shown that the increased circulating level of C-reactive protein (CRP) not only indicates the prevalence of cancer, but also is related to the increased risk of cancer in apparently healthy people in the future.
IR is considered to be a physiological adaptive response to pregnancy, fasting, exercise and acute stress environment, and also exists in various chronic diseases, such as obesity, type 2 diabetes (T2D) and cancer cachexia. Previous studies have shown that many novel, indirect, cheap and easily available alternative markers can fully predict IR, including the ratio of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (ldl-c/hdl-c, LHR), the ratio of total cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (tc/hdl-c), the ratio of triglycerides to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (tg/hdl-c), and the fasting triglyceride glucose (TYG) index. Among these indicators, the best IR prognostic indicators for cancer patients are still unclear.
Systemic inflammation and insulin resistance (IR) are usually associated with poor prognosis of cancer. The purpose of this study was to explore the prognostic value of alternative systemic inflammation and IR index in cancer patients.

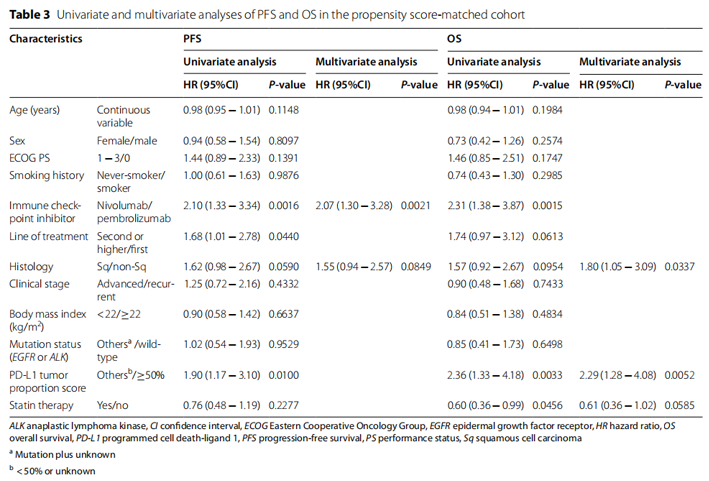
This multicenter prospective study included 5221 cancer patients with an average age of 59.41 ± 11.15 years, of whom 3061 (58.6%) were men. Alternative IR indices include the ratio of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LHR), the ratio of total cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TC / HDL-C), the ratio of triglycerides to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG / HDL-C), and fasting triglyceride glucose (TYG).
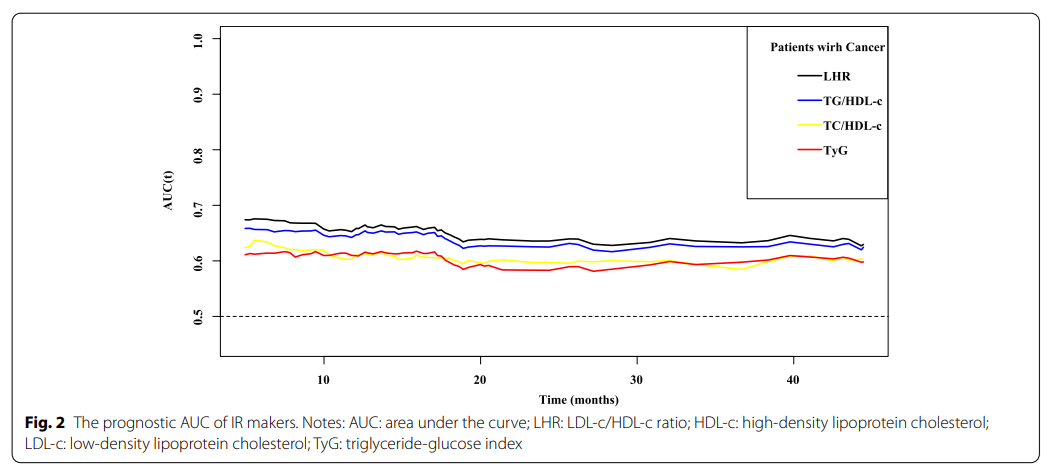
In this study, the median survival time of patients was 44.5 (40.5-51.4) months, and the total death during the 12-month period was 1115 (53.7%), with 196 death events per 1000 patient years of follow-up. ROC prognosis curve and C index showed that the prognosis value of LHR was better than other IR indexes.

Multivariable adjusted hazard ratio (HR) was higher in patients with high C-reactive protein (CRP) (HR, 1.51; 95% ci:1.38-1.65) and high LHR (HR, 1.20; 95% ci:1.06-1.37). The mortality of patients with high CRP and LHR is 1.75 times higher than that of patients with low CRP and LHR.

Overall, this study highlights the importance of systemic inflammation and IR in the prognosis of cancer patients. The prognostic value of LHR in cancer patients is better than TG / HDL-C, TC / HDL-C and TYG. In addition, the results of this study show that CRP and LHR can predict the survival of cancer patients. Both high CRP and high LHR predicted poor OS. The mortality of patients with high CRP and LHR is 1.75 times higher than that of patients with low CRP and LHR.
Source of original text:
Ruan GT, Xie HL, Gong YZ, Ge YZ, Zhang Q, Wang ZW, Zhang X, Zhang HY, Tang M, Song MM, Zhang XW, Yang M, Chen YB, Yu KY, Deng L, Wang KH, Cong MH, Shi HP. Prognostic importance of systemic inflammation and insulin resistance in patients with cancer: a prospective multicenter study. BMC Cancer. 2022 Jun 25; 22(1):700. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09752-5. PMID: 35752767; PMCID: PMC9233357.
Original link:
https://www.medsci.cn/article/show_article.do?id=bb66e310221f