Gastric cancer is the fifth most common cancer in the world and the third leading cause of cancer-related death. The incidence of gastric cancer in East Asian populations ranks first in the world. Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is considered to be the most important risk factor for gastric cancer.
Helicobacter pylori, abbreviated as HP, Helicobacter pylori, habitually known as Helicobacter pylori, H Pylori, with 2-6 flagella, is the only bacterium that can survive in the strong acid environment of the stomach. It lives between the gastric mucosa and the gastric mucosa epithelium and can actively invade the mucosal epithelial cells.
H. Pylori can cause chronic inflammation of the mucosa through bacteriology, cytotoxin and immune activation. Over time, it is anatomically manifested as epithelial damage. Repeated damage causes glandular withering, which then leads to atrophy of the gastric mucosa. With the passage of time or repeated infection with H.pylori, the probability and severity of mucosal atrophy increase, the mucosa becomes thinner, and the new epithelium becomes intestinal.
Eradication of Helicobacter pylori can reduce the risk of gastric cancer!
Intestinal metaplasia is considered to be an adaptive response of gastric mucosa to long-term adverse environment, and in the process of regeneration, heterologous intestinal epithelium further develops abnormally, forming atypical hyperplasia, which is manifested as cell heterotaxy and gland structure disorder. At present, the "chronic superficial gastritis - atrophic gastritis - intestinal epithelial metaplasia - atypical hyperplasia - gastric cancer" model has been recognized by most clinical scholars.
Recently, a study published in the journal gastroenterology evaluated the long-term impact of Helicobacter pylori eradication treatment on the incidence and mortality of gastric cancer in high-risk populations.

This is a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial conducted in the high risk area of gastric cancer in southern China. Since July 1994, a total of 1630 asymptomatic H. pylori infected patients were recruited and randomly (1:1) divided into groups to receive standard triple therapy (n = 817) or placebo (n = 813) for H. pylori eradication treatment, and then followed up until December 2020. The primary end point was the incidence of gastric cancer. Secondary endpoints were total mortality and cause specific mortality.
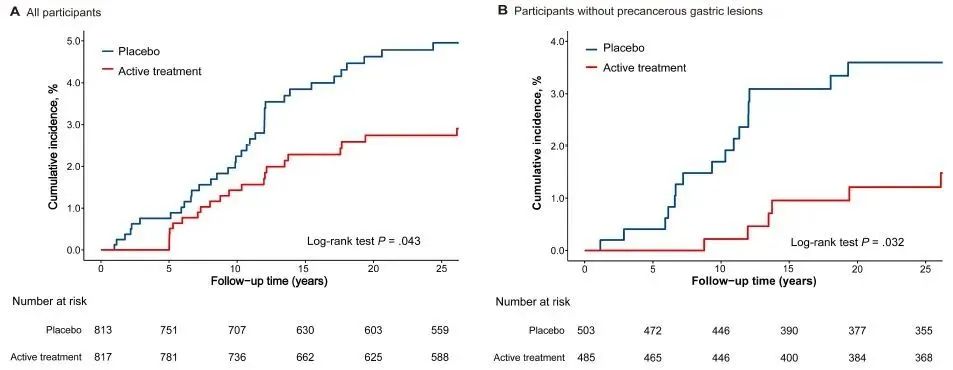
During the 26.5-year follow-up period, 21 (2.57%) and 35 (4.31%) subjects in the treatment group and placebo group were diagnosed with gastric cancer, respectively. The incidence of gastric cancer was lower in subjects treated with H. pylori compared with placebo (hazard ratio [hr] 0.57). In subjects without precancerous lesions of gastric cancer and dyspepsia symptoms at baseline, the reduction in gastric cancer risk was more significant after H. pylori eradication (HR 0.37 and 0.44, respectively). In addition, only 16 gastric cancers were found among 625 subjects who successfully eradicated H. pylori compared with 32 gastric cancers observed among 527 subjects with persistent H. pylori infection in the placebo group (HR 0.46). However, there was no significant difference between the two groups in any death endpoint.

Summary diagram
Therefore, eradication of Helicobacter pylori may have a long-term protective effect on gastric cancer in high-risk groups, especially for infected individuals without precancerous lesions.

So, how to eradicate HP?
H. As a infectious diseases, gastritis caused by H.pylori seems to be necessary for all H.pylori positive people to be treated. However, it should be noted that at present, the infection rate of H.pylori in China is still about 50%, and all H At present, it is difficult to achieve the treatment of pylori positive people, and at this stage, it is still necessary to follow the eradication of H Pylori indicators (the following table), so as to actively carry out H Pylori detection and treatment.
H. Pylori resistance is an important problem facing the world, and the situation of H.pylori resistance in China is more severe. Overall, H The resistance rate (including multidrug resistance rate) of pylori to clarithromycin, metronidazole and levofloxacin was on the rise, but the resistance rate to amoxicillin, tetracycline and furazolidone was still very low. The year-on-year increase in the resistance rate of traditional antibiotics has led to the continuous reduction of the eradication rate of the traditional triple regimen, which is no longer suitable for first-line H.pylori eradication in most regions of China.
The fifth national consensus report on the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection recommended the bismuth agent quadruple regimen as the main empirical treatment for the eradication of H.pylori, including a total of 7 regimens.

Note: a standard dose proton pump inhibitor + standard dose bismuth agent (2 times / D, oral administration hours before meal) + 2 kinds of antibacterial drugs (oral administration after meal). The standard dose of proton pump inhibitors are esmoprazole 20mg, rabeprazole 10mg (or 20mg), omeprazole 20mg, lansoprazole 30mg, pantoprazole 40mg, and iprazole 5mg, whichever is more; The standard dose of bismuth agent is 220mg bismuth potassium citrate (the standard dose of bismuth pectin is to be determined); B according to Graham's grading, the curative effect is 85% - 90% in Grade C and 90% - 94% in Grade B
Except that the regimen containing levofloxacin is not used as the primary treatment regimen, eradication treatment does not include first-line and second-line treatments, and the regimen with high efficacy should be used for the primary treatment as far as possible. Most areas in China are highly resistant to antibiotics, and the recommended course of empirical bismuth quadruple therapy is 14 days, unless local studies prove that 10 days of treatment is effective (eradication rate > 90%). The selection of antimicrobial combination in the eradication plan should refer to the H.pylori resistance rate monitored in the local population and the personal antimicrobial use history.
In addition, the selection of the scheme should weigh the efficacy, cost, potential adverse reactions and drug availability, and make an individual choice. After the initial treatment fails, one of the other schemes can be selected for remedial treatment. The scheme shall be selected according to the local H Pylori antimicrobial resistance rate and personal drug use history, weighing efficacy, drug cost, adverse reactions and drug availability.
Even H After the complete cure of pylori, we can't relax. If we don't pay attention to it, there is still the possibility of recurrence.
Source link:
https://www.medsci.cn/article/show_article.do?id=55f7e38267c1