Blood routine examination is one of the most commonly used clinical examinations, and the results of blood routine examination also hide secrets related to cancer prognosis. Today, Xiaobian will take you to read the blood routine test results to see which tumor secrets are hidden.
The indicators related to prognosis in the blood routine report are mainly: absolute number of lymphocytes (ALC), neutrophil / lymphocyte ratio (NLR), lymphocyte / monocyte ratio (LMR), platelet / lymphocyte ratio (PLR).
Low NLR value, high LMR value and low PLR value are related to the long overall survival of patients with various solid tumors; However, different tumors have different "sensitivity" to these three indicators, which are described in detail below.
1. Breast cancer
Many studies have reported the relationship between the above four blood routine results and the prognosis of breast cancer.
Recently, in 114 patients with HER2 negative advanced breast cancer (mostly er+) who received Pb regimen, some scholars retrospectively analyzed and discussed the relationship between blood routine lymphocyte related indicators and the prognosis of Pb therapy. Treatment failure time (TTF) and overall survival (OS) were the main survival indicators analyzed in this study. These two survival indicators are that the longer the better, indicating the better prognosis of patients.
The results showed that the absolute number of lymphocytes (ALC) >1500/ μ 50. Lymphocyte / monocyte ratio (LMR) > 3, neutrophil / lymphocyte ratio (NLR) ≤ 3, platelet / lymphocyte ratio (PLR) ≤ 300 are all related to TTF, that is, patients have a long time to benefit from the efficacy.
This suggests that these blood routine indicators may predict the therapeutic benefit time of HER2 negative advanced breast cancer patients receiving Pb.
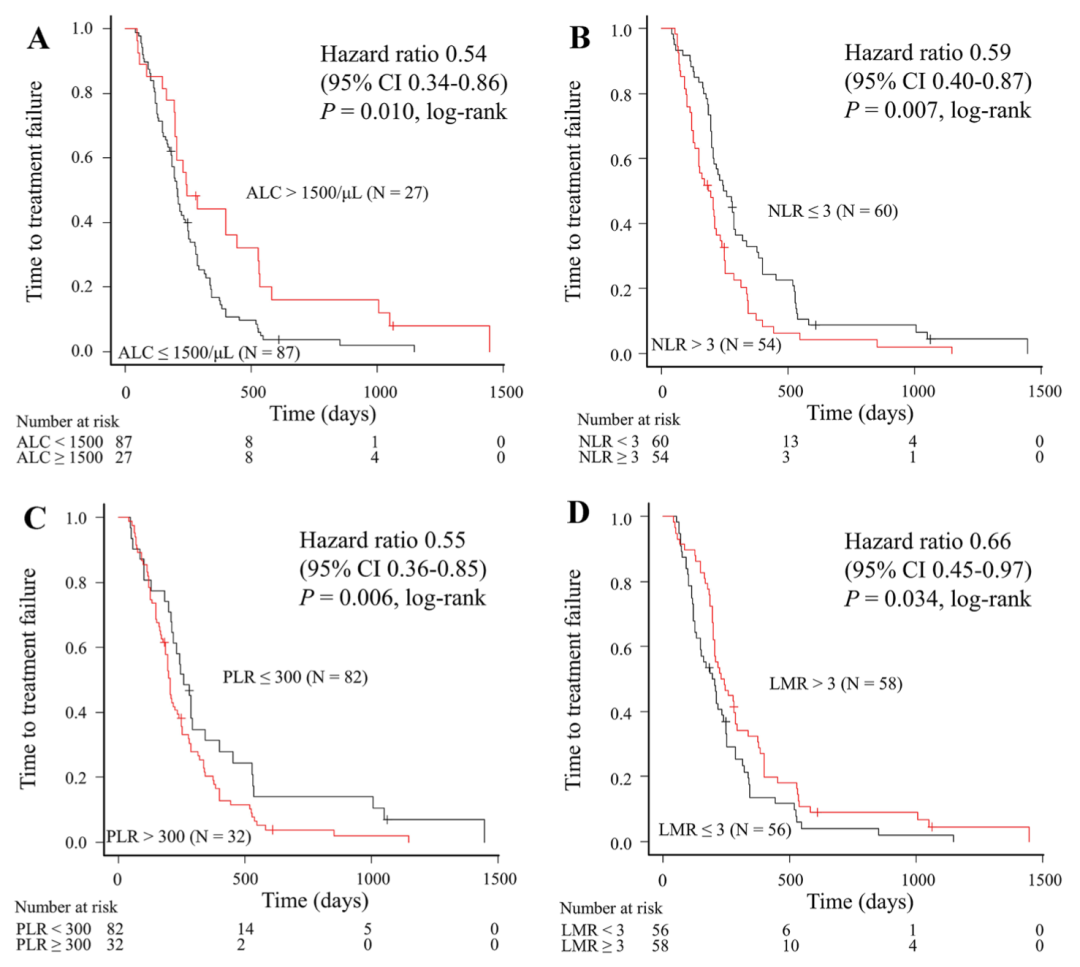
Figure 1 Relationship between four blood routine indicators and time to treatment failure (TTF)
(A)ALC; (B)NLR; (C)PLR; (D)LMR
Overall survival is the "gold standard" for tumor survival benefits, so are the four blood routine indicators also related to overall survival? The result is similar. Through the survival analysis curve, we found that the absolute number of lymphocytes (ALC), lymphocyte / monocyte ratio (LMR) and neutrophil / lymphocyte ratio (NLR) were correlated with the overall survival, which was statistically significant. Platelet / lymphocyte ratio (PLR) also showed a certain correlation, but not as significant as the other three (Fig. 2).
Similar to the time of efficacy benefit, alc>1500/ μ 50. LMR > 3 and NLR ≤ 3 are also associated with longer overall survival, suggesting that multiple lymphocyte related indicators may have a predictive effect on the prognosis of patients with HER2 negative advanced breast cancer.
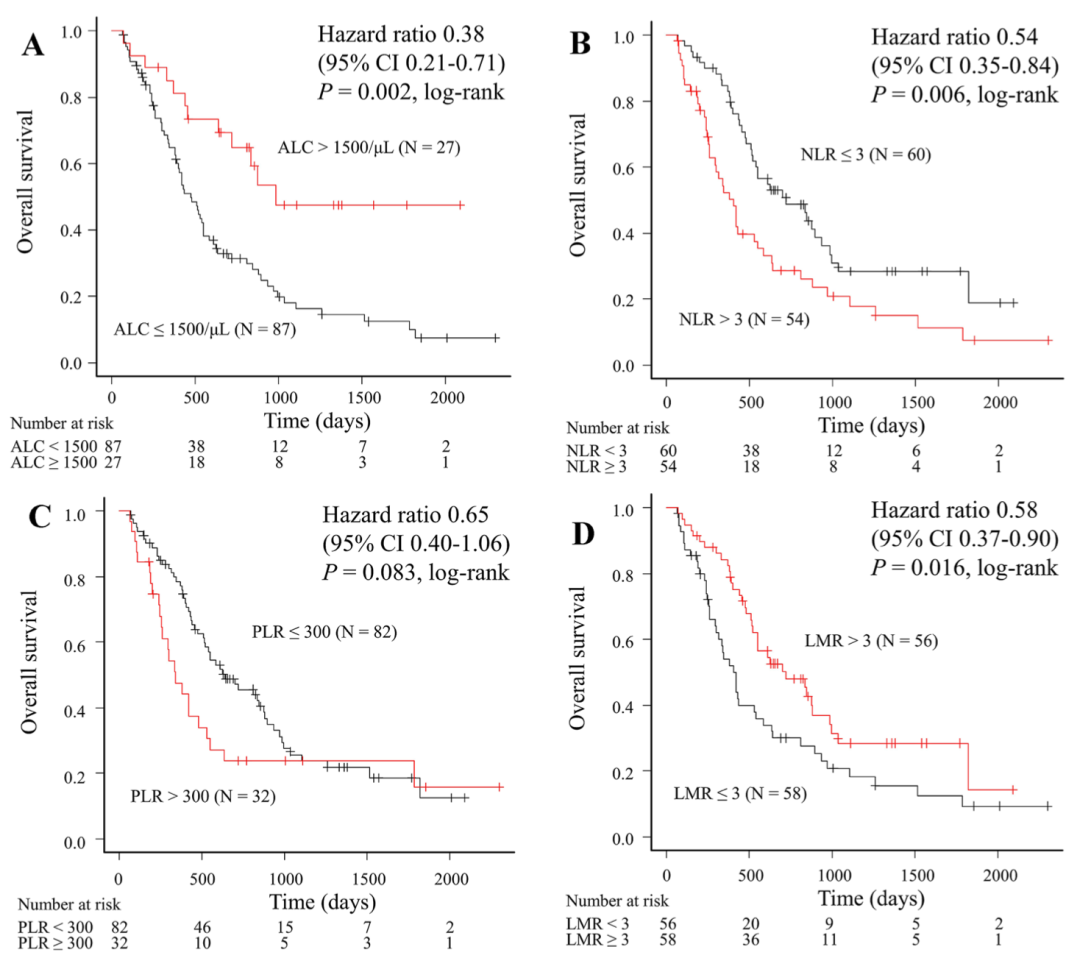
Figure 2 Relationship between four blood routine indicators and overall survival (OS)
(A)ALC; (B)NLR; (C)PLR; (D)LMR
Other situations
Patients using aribrin can focus on two indicators: ALC and NLR. High ALC value and low NLR value are related to long overall survival.
For patients with estrogen receptor ER negative and HER-2 negative breast cancer, studies have shown that NLR value is more valuable in predicting prognosis. Patients with low NLR have better prognosis.
For breast cancer patients in Asia, the higher PLR value may be related to the shortening of overall survival and HER-2 positive, which can be used as an indicator of poor prognosis in breast cancer patients.
2. Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
NLR value: the 5-year survival rate of patients in the high NLR group was 19.1%; The 5-year survival rate of patients in the low NLR group was 47.07%. (very different)
LMR value: the 5-year survival rate of patients in the high LMR group was 57%; The 5-year survival rate of patients in the low LMR group was 26%. (very different)
PLR value: the 5-year survival rate of patients in high PLR group was 40.15%; The 5-year survival rate of patients in the low PLR group was 42.98%. (almost no difference)
Conclusion: NLR and LMR have great reference significance for the prognosis of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. The survival time of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma whose blood routine NLR ≥ 2.46 and LMR < 3.88 may be shorter.
3. Colon cancer
The following experiments mainly compared the relationship between preoperative blood routine examination and postoperative 5-year survival rate of colon cancer patients.
NLR value: the 5-year survival rate of patients in the high NLR group was 37.8%; The 5-year survival rate of patients in the low NLR group was 83.1%. (very different)
LMR value: the 5-year survival rate of patients in the high LMR group was 73.2%; The 5-year survival rate of patients in the low LMR group was 50%. (there are differences)
PLR value: the 5-year survival rate of patients in high PLR group was 49.4%; The 5-year survival rate of patients in the low PLR group was 74.8%. (there are differences)
Conclusion: high NLR, high PLR and low LMR before operation are risk factors for prognosis of locally advanced colon cancer, among which high NLR (> 3.25) is an independent risk factor. The experiment also showed that patients with gastric cancer had a lower NLR value before operation and a longer survival time after operation (compared with the data of patients with colon cancer).
4. Squamous cell carcinoma of cervix
NLR value: the median progression free survival of patients in the high NLR group was 19 months; The median progression free survival of patients in the low NLR group was 32 months. (there are differences)
LMR value: the median progression free survival of patients in the high LMR group was 36 months; The median progression free survival of patients in the low LMR group was 19 months. (very different)
PLR value: the median progression free survival of patients in the high LMR group was 22 months; The median progression free survival of patients in the low LMR group was 30 months. (the difference is not too great)
Conclusion: NLR, LMR and PLR are the prognostic factors of cervical cancer patients, among which LMR is an independent risk factor. When LMR < 5.19, the prognosis of patients may be poor. (the subjects of this experiment are all patients with stage IIB cervical squamous cell carcinoma)
5. Ovarian cancer
The blood routine data selected in the experiment was added with one item - "red blood cell distribution width (RDW)".
Research findings:
NLR, RDW, PLR: compared with patients with benign ovarian tumors, these three values are higher in patients with ovarian cancer; 3. These three values of patients with stage IV cervical cancer are also higher than those of patients with stage I and II cervical cancer.
LMR: Contrary to the above three values, the higher the malignant degree of the tumor, the lower the value.
6. All solid tumors
The lower PLR value is related to the longer overall survival of patients with various solid tumors.
The higher LMR value is related to the longer overall survival of patients with various solid tumors.
NLR value: whether the treatment plan is surgery, neoadjuvant + surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy or non surgery, the increase of NLR value is related to poor prognosis.
Lymphocyte related indexes have independent predictive value for cancer prognosis
We can see that most of the four blood routine indicators are related to survival indicators; However, other clinicopathological factors, such as metastasis location and treatment, may also affect prognosis (Table 1). So, do these blood routine indicators have independent predictive value for cancer prognosis? Let's take a look at the results of multifactor analysis.
Table 1 univariate analysis of prognostic factors

Through multifactor analysis, we can see that alc>1500/ μ 50. NLR ≤ 3, PLR ≤ 300 are independently related to TTF benefits; Alc>1500/ μ 50. NLR ≤ 3 and LMR > 3 were independently associated with overall survival benefit. This shows that these blood routine indicators can better predict the prognosis of patients.
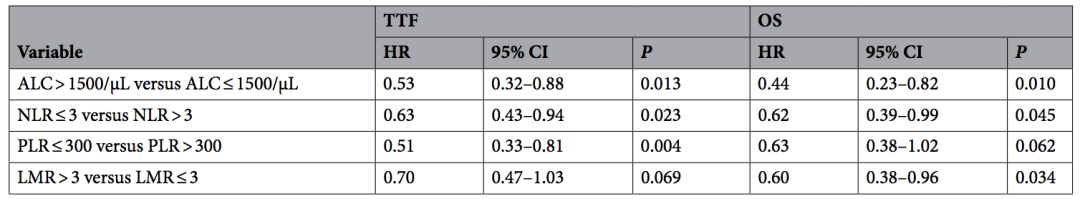
Table 2 results of multifactor analysis of TTF and OS
Blood routine test is relatively simple, and it can also be detected dynamically and in real time. It is of great significance for monitoring cancer treatment and guiding prognosis. It is hoped that there will be more large-scale studies in the future to further determine the value of these indicators and better help cancer treatment.
Reference:
Shogo Nakamoto, Masahiko Ikeda, Shinichiro Kubo, et al. Systemic immunity markers associated with lymphocytes predict the survival benefit from paclitaxel plus bevacizumab in HER2 negative advanced breast cancer. Sci Rep. 2021; 11(1): 6328. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85948-2.
Article source:
https://www.medsci.cn/article/show_article.do?id=9fade329849c