The incidence rate of breast nodules is getting higher and higher. Most solid breast nodules are mainly hypoechoic lesions found by ultrasound, often benign. But some of them are breast cancer, so the grading of breast nodules is particularly important.
What is the grading of breast nodules?
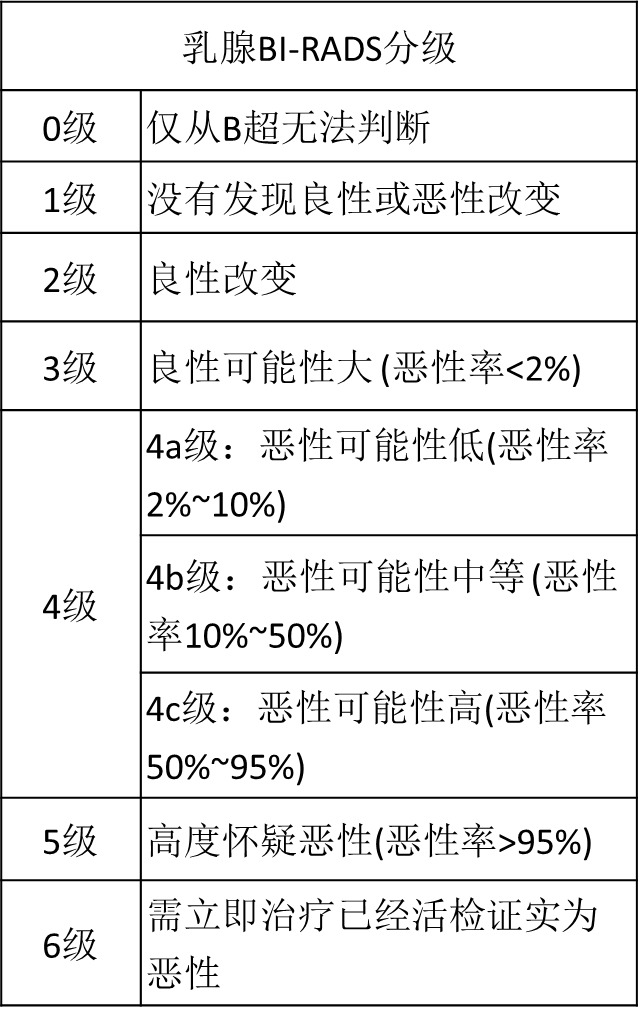
Once a breast nodule is found by color Doppler ultrasound, an interview will be conducted according to the shape of the breast nodule, that is, the risk of the breast nodule will be scored. The BI-RADS grading method divides the breast lesions into 0 ~ 6 grades. Generally speaking, the higher the grade, the greater the possibility of malignancy.
1. those with clear boundary and neat appearance will be classified as grade 2 or grade 3, and considered as relatively good nodules with low risk;
2. if the boundary is not so clear, not beautiful and the shape is not so regular, it may be classified as 4a, indicating that this nodule is slightly suspected and needs further examination to prove whether it is a good nodule. Of course, with the bad shape and the increase of risk, there are scores of grade 4b, 4C, 5 and 6.
Today, let's talk about BI-RADS rating.
BI-RADS is the abbreviation of breast imaging reporting and data system of American Radiological Society. The BI-RADS grading standard was jointly formulated by the National Cancer Institute, the Centers for Disease Control and prevention, the food and drug administration, the American Medical Association, the American Society of surgeons, the American Society of pathologists and the American Society of radiology. The establishment of this standard makes the characteristic terms for describing breast lesions and the reporting terms for evaluating the malignancy of lesions tend to be standardized, and reduces the errors and uncertainties in understanding and reading breast imaging reports, especially for the reexamination and diagnosis of breast cancer.
The classification mainly describes breast tumors from the aspects of morphology, orientation, edge, internal echo, posterior characteristics, relationship with surrounding tissues, calcification, etc.
Irregular shape, aspect ratio greater than 1, blurred edges (angulation, microlobulation, "crab foot process"), heterogeneous hypoechoic, posterior echo change, structural disorder invading surrounding tissues, and calcification are considered as malignant signs.
Normal breast tissue
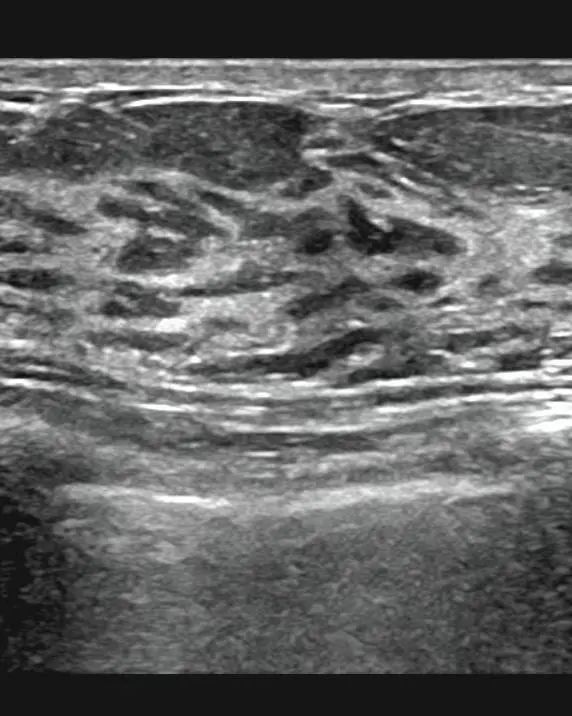
BI-RADS classification standard
Level 1: negative
No abnormal findings are found (if there are normal intramammary and preaxillary lymph nodes, they also belong to class 1).
Routine physical examination (once a year) is recommended.
Grade 2: benign lesions
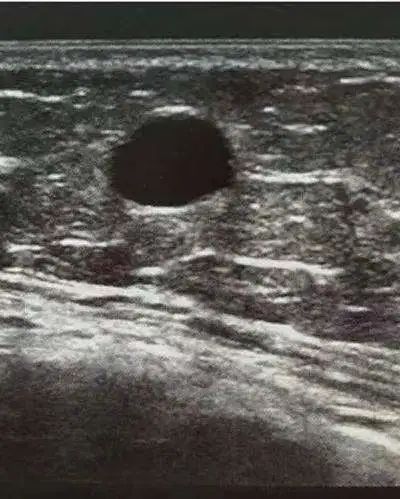
Simple cyst and galactocele; Breast implants;
Stable postoperative changes;
Fibroadenoma without change after follow-up.
If the mammary gland is compared to a bunch of grapes, the breast cyst is like a grape in it. It is all grape juice, and there is no pulp.
Regular follow-up (every 6 months to 1 year) is recommended.
Level 3: benign may be large
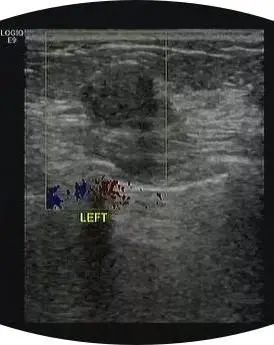
It includes solid mass with smooth margin, round or oval shape and transverse diameter larger than high diameter, which is likely to be fibroadenoma;
Complex cysts and clustered microcapsules with negative palpation.
Breast fibroadenoma is equivalent to finding that a grape has lost its original normal structure, only the dried pulp
Short term follow-up (once every 3-6 months) is recommended. Those who have not changed in the two-year follow-up can be reduced to category 2
Grade 4: suspected malignancy
It is equivalent to that we found a grape broken.
Pathological examination (such as fine needle aspiration cytology, hollow core needle aspiration biopsy and surgical biopsy) is recommended to make a definite diagnosis.
4A: low degree suspicious malignancy (≥ 2%- ≤ 10%). The pathological results are generally non malignant. 6 months or routine follow-up should be carried out after obtaining benign biopsy or cytological results. For example, palpable, locally well-defined solid masses, ultrasound features suggest fibroadenoma; Palpable complex cyst or possible abscess.

4b: moderately malignant lesions (> 10% to ≤ 50%). Imaging examination and pathological results should be combined. Some well-defined and some poorly defined fibroadenomas or fat necrosis can be followed up, but papillomas may need resection and biopsy.
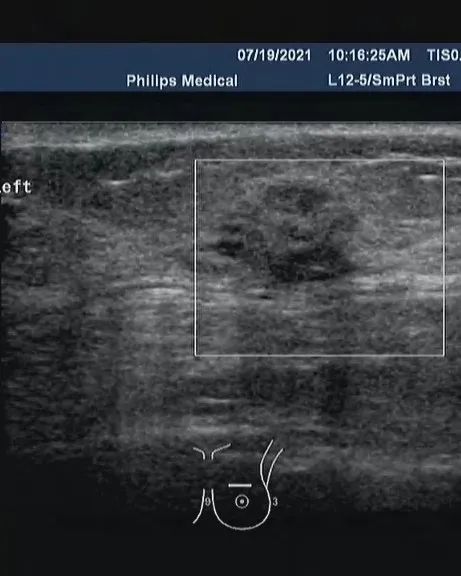
4C: malignant may be large (> 50% to ≤ 95%), but not as typical as grade 5. For example, irregular solid mass with unclear boundary or new cluster fine pleomorphic calcification. This grade of lesion is likely to be the result of malignancy.

Grade 5: highly suspicious malignancy
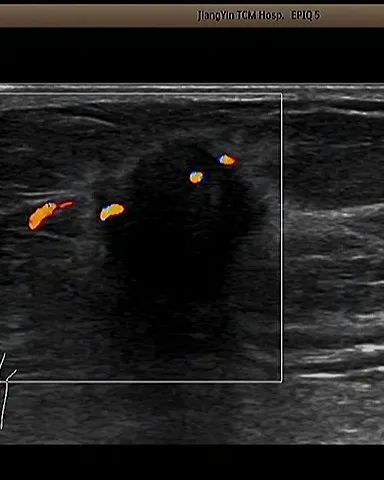
Appropriate clinical measures should be taken (almost certainly malignant). Ultrasound has characteristic abnormal signs, and the risk of malignancy is greater than 95%. Definitive treatment should begin.
When sentinel lymph node imaging and neoadjuvant chemotherapy are considered, image-guided hollow core needle biopsy should be performed to obtain histological diagnosis.
Category 6: malignant confirmed by biopsy
Appropriate clinical measures should be taken. This classification is used for imaging evaluation of biopsy proved malignant but not yet treated. It is mainly to evaluate the imaging changes after biopsy or monitor the imaging changes of neoadjuvant chemotherapy before operation.
Sum up, easy to save!
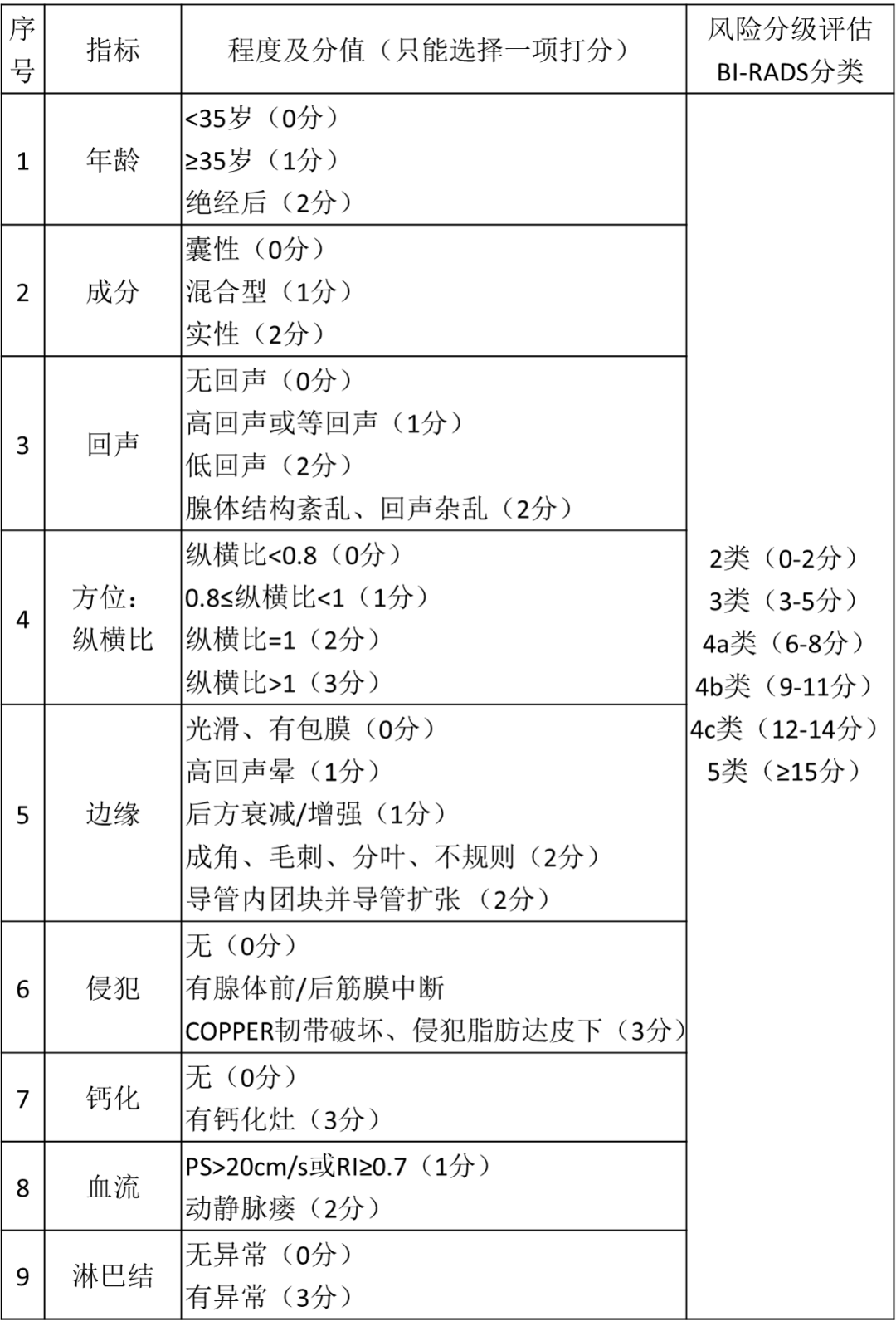
In addition, the quantitative assessment form of breast nodule risk classification is attached, which can more accurately diagnose the classification of breast nodule.
Original link:
https://www.medsci.cn/article/show_article.do?id=a0aee2660563