1、 How to predict the growth rate?
Most of the ground glass nodules in the lung grow slowly. In clinical diagnosis and treatment, a very important aspect is to predict the growth trend of ground glass nodules in the next five years. It is of great significance to choose whether to operate or not. If the probability remains stable for 5 years, the current recommended follow-up strategy is relatively safe.
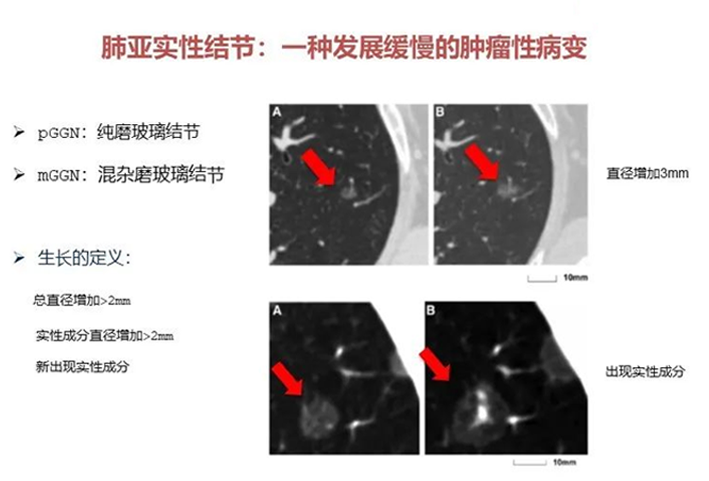
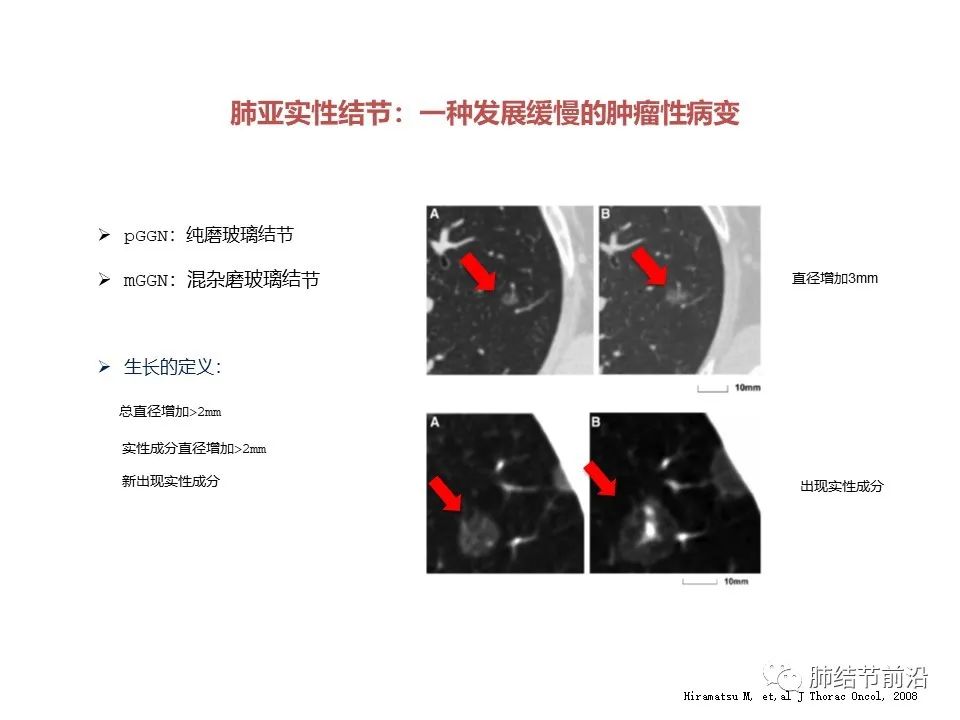
First, the growth of lung ground glass nodules is defined. If the following conditions are met, it can be clearly defined as the growth of pulmonary nodules.
Pure ground glass nodule, with the diameter increased by more than 2mm;
The solid component increased by more than 2mm;
New solid ingredients appear.
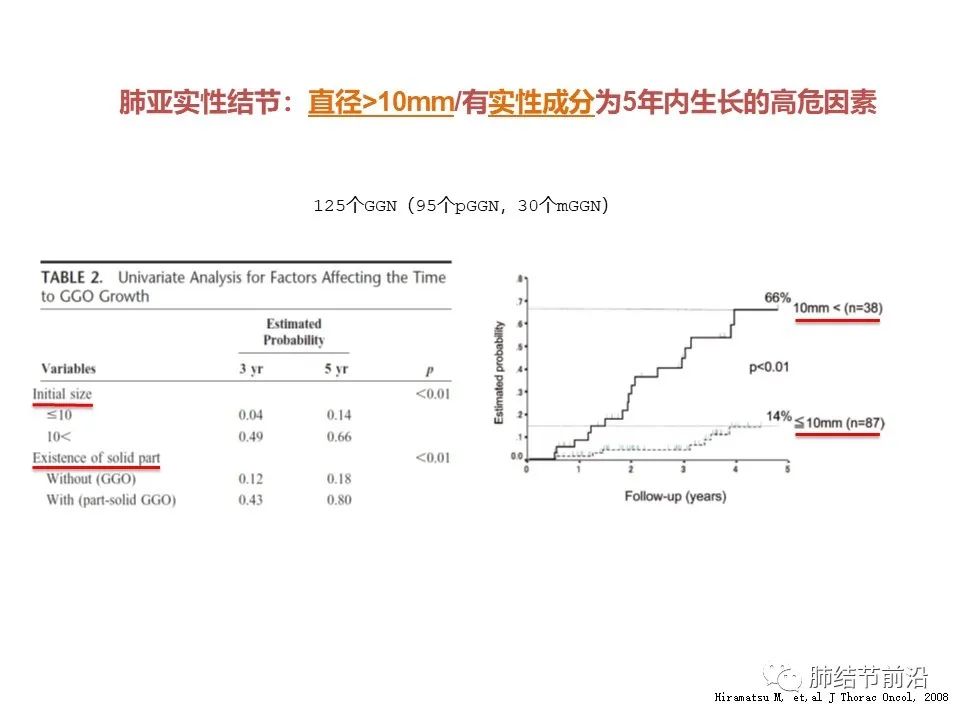
What is the probability of the growth of ground glass nodules within 5 years? This article counted 125 ground glass nodules and found that the overall probability of growth within 5 years was about 30%.

So which kind of nodule is at higher risk of growth?
Pure ground glass nodule >10mm;
Or there are solid components (i.e. mixed ground glass nodules).
For pure ground glass nodules with a diameter of >10mm, the probability of growth within 5 years is 66%, and for ground glass nodules with a diameter of <10mm, the probability of growth is only 14%.
All pure ground glass nodules have a 5-year growth probability of 18%, and mixed ground glass nodules have a 5-year growth probability of 80%.
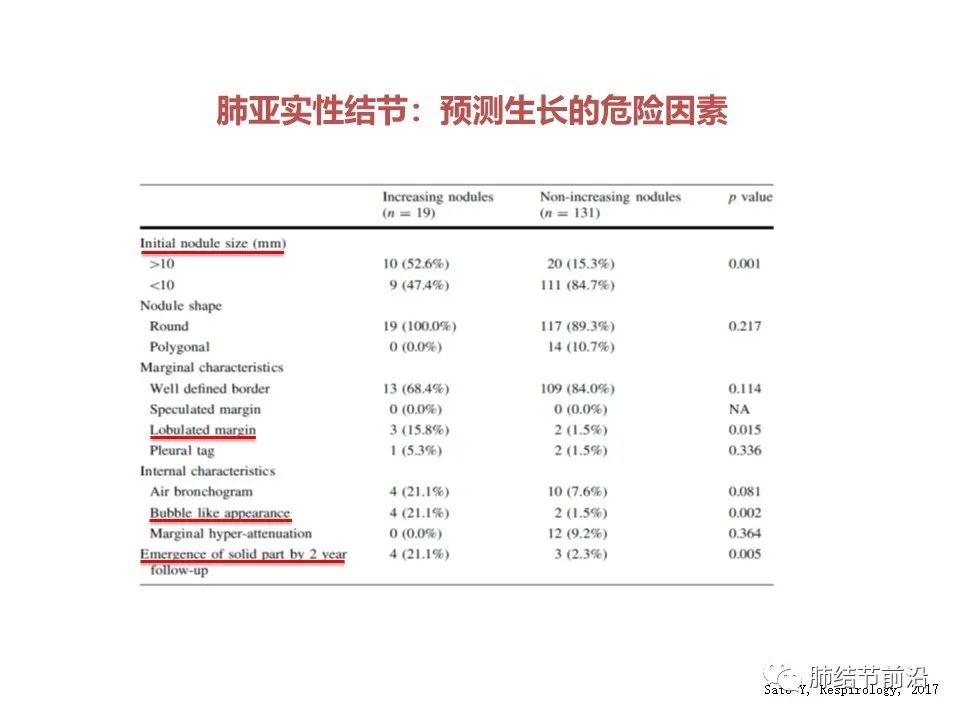
Another study also made five-year growth predictors of ground glass nodules. Similarly, >10mm was used as a predictor of growth. Above 10mm, the probability of 5-year growth is 52.9%, below 10mm, the probability of 5-year growth is only 15.3%.
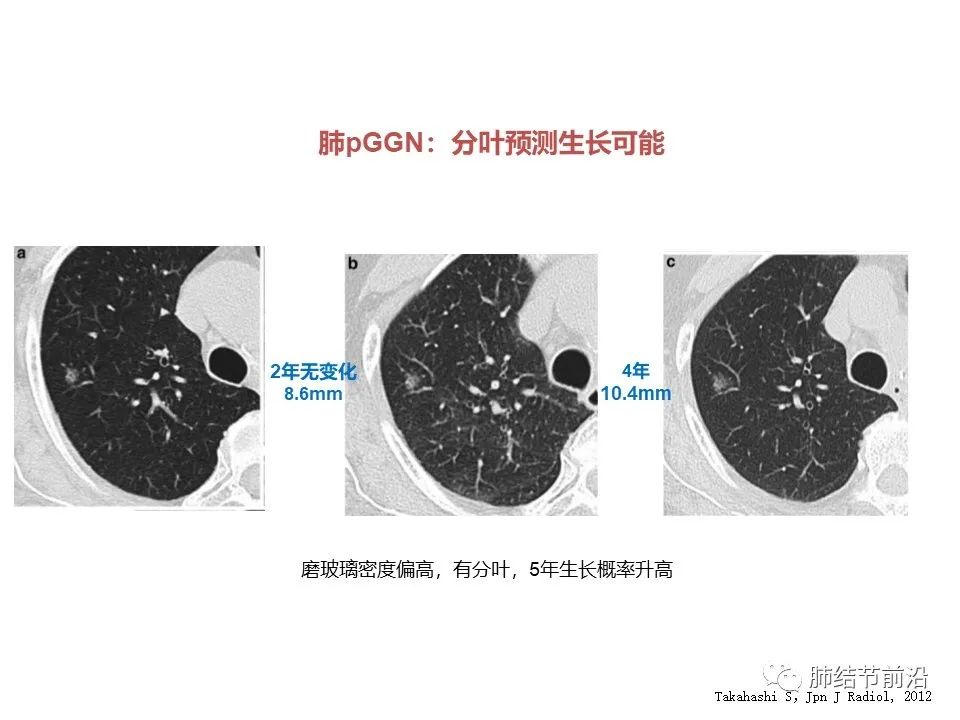
In addition, some CT features may also predict the positive growth risk of ground glass: lobulation, cavitation, and new solid components within 2 years.
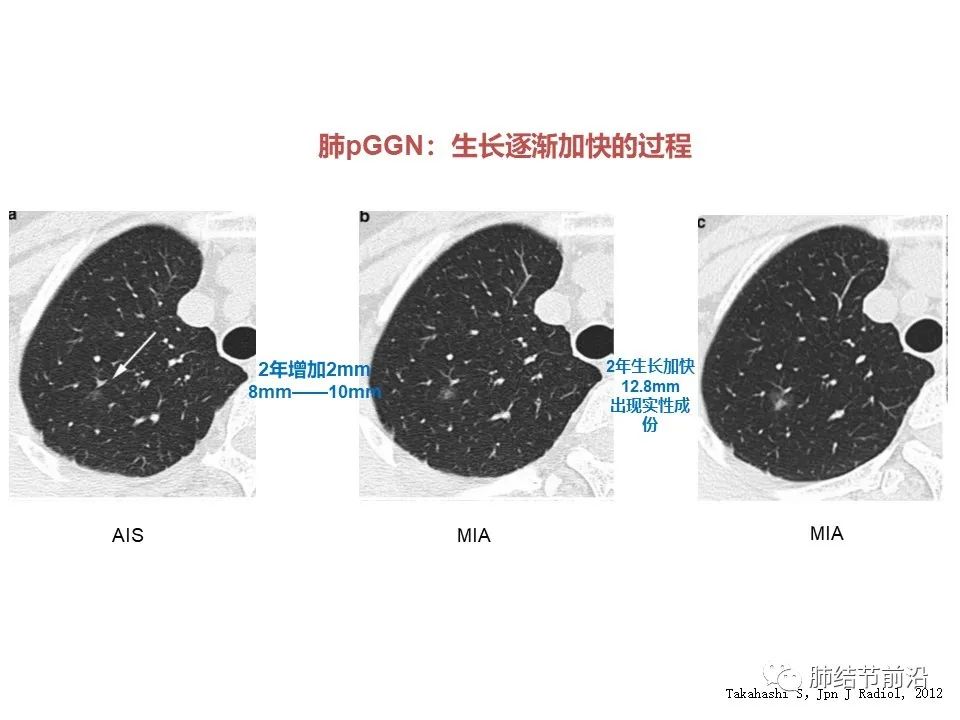
In other words, after the solid components appear, the nodules may continue to grow in the next five years.
In addition, the density of the glass grinding class is also an important indicator of growth prediction. According to research statistics, the 5-year growth probability of nodules with an average CT value lower than -670hu is only 6.8%. The 5-year growth probability of nodules with CT value higher than -670 is as high as 68.4%, with significant difference.
And -670 is the density of carcinoma in situ, that is to say, the probability of growth within 5 years is very small for carcinoma in situ with low density.

Of course, the density of -670 as the standard is too low. We suggest that the CT value of -300 to -400 be used clinically as a high-risk factor for the growth of ground glass nodules within 5 years.
In addition, there are some possible but unconfirmed high-risk factors for the growth of pulmonary ground glass nodules, such as men, smoking history, emphysema, etc. The family history of lung cancer has not been confirmed as a risk factor for the growth of ground glass nodules.
Let's take a look at some typical examples:
1. 6mm low-density pure ground glass nodules that have not changed for 8 years.

2. The density of ground glass nodules is high, about -400, with shallow lobulation, which may grow. Follow up results: 2mm growth in 4 years.
3. Solid components appear, and the subsequent growth is accelerated.
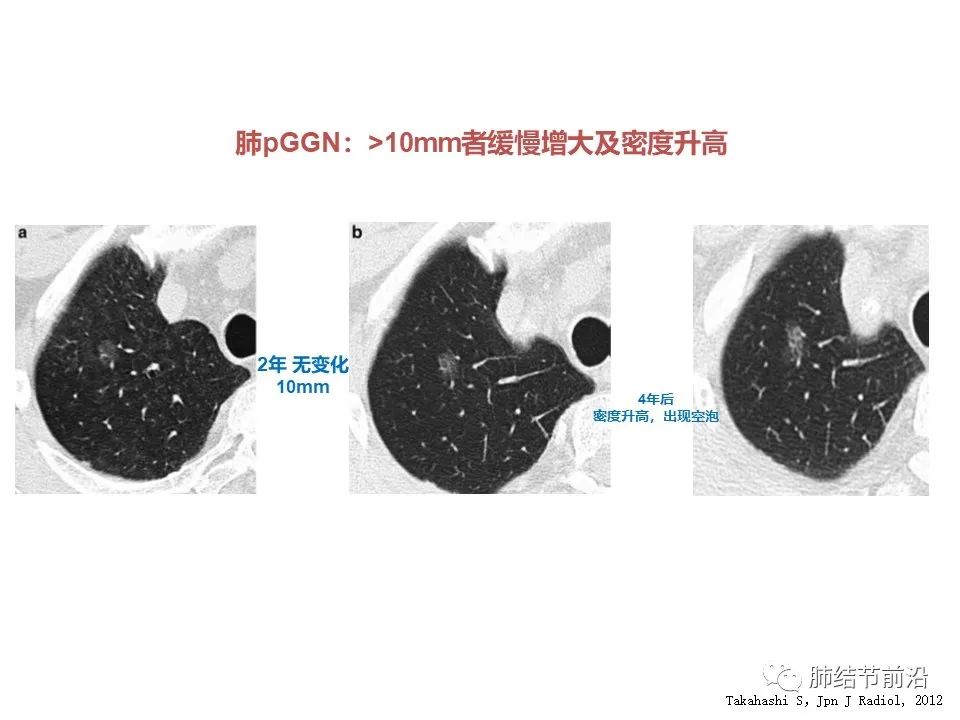
4. Pure ground glass nodules with a diameter of >10mm have a higher probability of growth within 5 years, from 10mm to 13.4mm.

5. Pure ground glass nodules with diameter >10mm did not grow for 2 years, but increased in growth and density in 4 years.
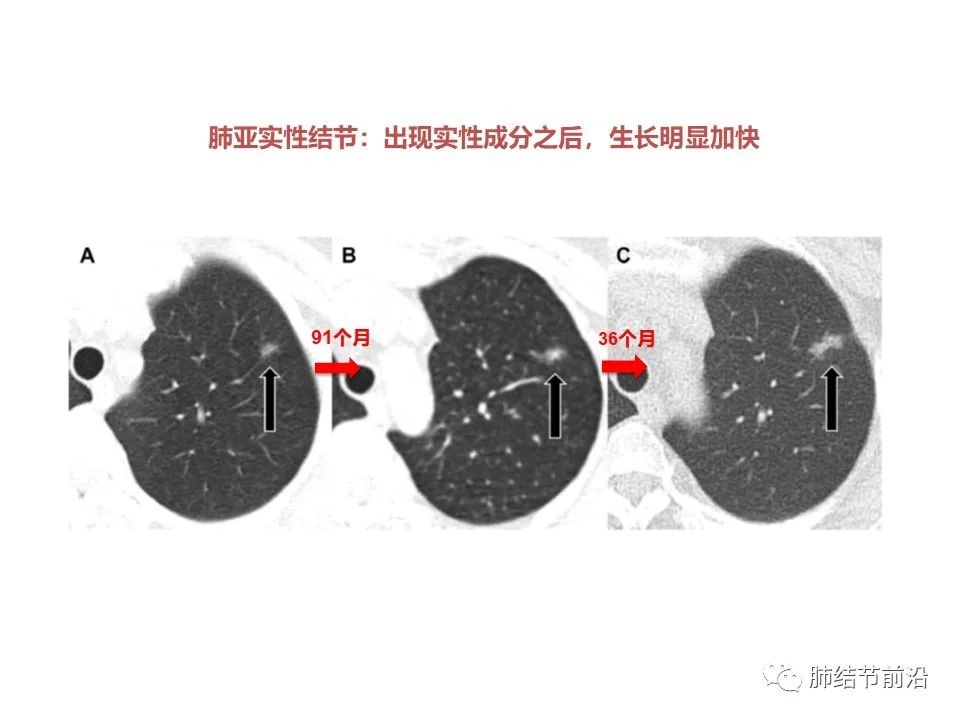
6. The pulmonary ground glass nodule is 8mm, but the density is high, and the CT value is estimated to be about -400. Solid components appeared in 7-year follow-up, and then accelerated to 12mm in 3 years.
To sum up, at present, the possible growth prediction indicators for ground glass nodules within 5 years are:
Pure ground glass nodule >10mm;
Mixed ground glass nodules (with solid components);
The CT value is higher than -400, especially the ground glass nodules higher than -300;
CT images showed vacuoles and lobulation.
Among them, the meaning of density is higher than that of diameter. The density of pulmonary ground glass nodules that have been found in clinic for 1-2 years is basically higher than -300.
Men, smokers, emphysema. These factors have not been recognized as indicators of the growth of ground glass nodules. The vascular abnormalities in CT have not been confirmed as growth predictors, which need further analysis and summary.
2、 Risk of lymph nodes and distant metastasis
Another important content in the diagnosis of pulmonary nodules is to judge the possibility of lymph nodes and distant metastasis. This has important predictive significance for the choice of surgical timing and the scope of lymph node dissection. If there is a risk of metastasis, the diagnosis should be as clear as possible, not long-term follow-up.
First, solid nodules of any size may have a small probability of lymph nodes and distant metastasis. Clinically, there may be distant metastasis of solid nodules <10mm in the lung, and even distant metastatic lesions that cannot be found in the lung by CT. Therefore, here we only discuss sub solid nodules, namely pure ground glass nodules and mixed ground glass nodules.
First, pure ground glass nodules have little possibility of metastasis. In our statistics, 344 cases of pure ground glass nodules, even invasive adenocarcinoma, were all stage IA, and there were no cases of lymph nodes or distant metastasis. At present, there is no case report of lymph nodes and distant metastasis in pure ground glass nodules in other literatures.
Second, CTR (consolidation to tumor ratio), that is, the ratio of the diameter of solid components of pulmonary nodules to the maximum diameter of nodules, can be used to predict the risk of lymph nodes and distant metastasis of mixed ground glass nodules. In the study from Taiwan Province, ctr=0.62 was used as a possible indicator of lymph node metastasis. The probability of postoperative lymph node metastasis (n1+n2) in 258 patients with ctr<0.62 was only 1.9%. For pulmonary nodules with CTR ≥ 0.62, the probability of lymph node metastasis (n1+n2) increased to 10.4%.
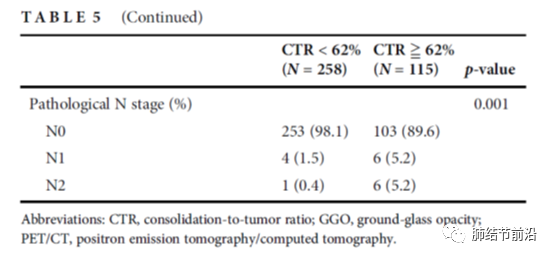
The data of the Department of thoracic surgery of Zhongshan Hospital are similar. According to CTR, sub solid nodules are divided into four groups a/b/c/d, as shown below:
Group A (CTR ≤ 0.25):442 cases
Group B (0.25<ctr ≤ 0.5):210 cases
Group C (0.5<ctr ≤ 0.75):173 cases
Group D (0.75<ctr<1): 37 cases
The data of lymph node metastasis is like this. No lymph node metastasis was found in group a/b/c, and only in group D with ctr>0.75, the probability of lymph node metastasis was 5.4%.

In addition, we can also find the data of lymph node metastasis probability of lung sub solid nodules from two classic studies in Japan, jcog0804 and jcog0802.
Jcog0804: among 333 cases of pulmonary nodules within 2cm with ctr<0.25, 314 cases were tumor lesions after operation, in which no lymph node metastasis or distant metastasis was found, all of which were stage IA.
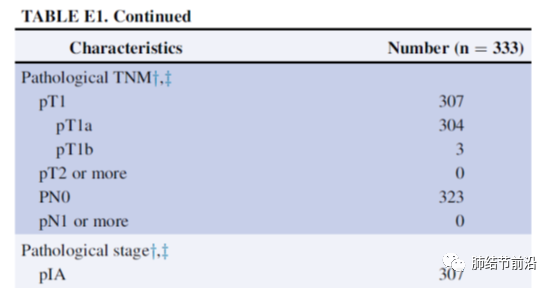
In jcog0802, lung nodules with a total diameter of less than 2cm and a ctr>0.5 were included. Among them, there were 65 cases of lymph node metastasis in 1038 patients, that is, 65/1038=6.3%. Ctr>0.5 also brings the risk of distant metastasis. Among 1038 patients, only 1 (0.1%) was confirmed as distant metastasis.

Based on the clinical data analysis of some large samples above, we can think that:
Pure ground glass nodules rarely have lymph nodes and distant metastasis.
Nodules with ctr<0.25 within 2cm, that is, mixed ground glass nodules with solid components <5mm, rarely have lymph nodes and distant metastasis.
Ctr<0.5, the probability of lymph node and distant metastasis is still very low.
Ctr>0.5, the probability of lymph node metastasis is about 5-10%, and the possibility of distant metastasis begins to appear.
Ctr>0.5, the probability of distant metastasis increased, but the overall is still very low, less than 1%.
Within 2cm, the probability of metastasis of pulmonary nodules with ctr<0.5 is very low, while those with ctr<0.25 almost have no metastasis.
These data from the Asian population can not only be used as a reference for us to recommend whether to operate or not, but also as a theoretical basis for the pure ground glass nodules and pulmonary nodules with ctr<0.25, which do not need lymph node dissection in surgery, and even radical intervention and local minimally invasive ablation in the future.
3、 Which pulmonary nodules will not recur?
For early pulmonary nodules, the goal of treatment should be complete cure. In recent years, many research data have confirmed that the prognosis of pulmonary sub solid nodules after surgery is good. The postoperative no return survival rate (RFs) and overall survival rate (OS) are much better than the historical data of previous stage IA lung cancer surgery. Therefore, the 5-year OS data in previous TNM staging can no longer be used to judge the recurrence and survival probability of current patients. It can even be said that most of the pulmonary sub solid nodules will hardly recur after operation, and even will not affect life. At present, the prediction of postoperative RFs or OS can be judged from two aspects: postoperative pathological classification and preoperative CT image characteristics.
So which lung cancer can be considered basically safe after resection? First of all, for patients with lung adenocarcinoma in situ or micro invasive adenocarcinoma after surgery, it can be considered that there will be no recurrence.
Meta analysis published in the journal clinical lung cancer in 2016 showed that 429 patients with carcinoma in situ and 294 patients with microinvasive adenocarcinoma had no recurrence in 5 years after operation (rfs=100%).

In 2021, jto magazine published the data of longer follow-up. The conclusion is: 207 cases of carcinoma in situ and 317 cases of microinvasive adenocarcinoma, the estimated 10-year recurrence probability is 0.

The same is true of large sample data from China. Data from Shanghai Chest Hospital published in JTD magazine in 2020 showed that 412 cases of lung carcinoma in situ and 675 cases of microinvasive adenocarcinoma had no recurrence in 5 years after operation.

In addition, for pure ground glass nodules, regardless of size and pathological type, postoperative recurrence may be very small. In other words, it is very safe to remove pure ground glass nodules, even if the postoperative pathology is invasive adenocarcinoma.
Data from Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital showed that in 273 pure ground glass nodules confirmed by pathology as invasive adenocarcinoma after operation, no recurrence was found, regardless of the diameter, even if it was more than 30mm. Of course, the sample size of this study is slightly small. In addition, in the data of this study, we can also see that even if the pure ground glass nodules are invasive adenocarcinoma, there are no cases of vascular invasion. Therefore, there is no data support for the claim that metastasis will occur as long as there is "blood vessel passing through" in the ground glass nodule. The "blood vessel passing through" of this ground glass nodule is often overemphasized and interpreted at present.

In addition, we can further expand the range of nodules with very good postoperative prognosis: some mixed ground glass nodules have very good prognosis.
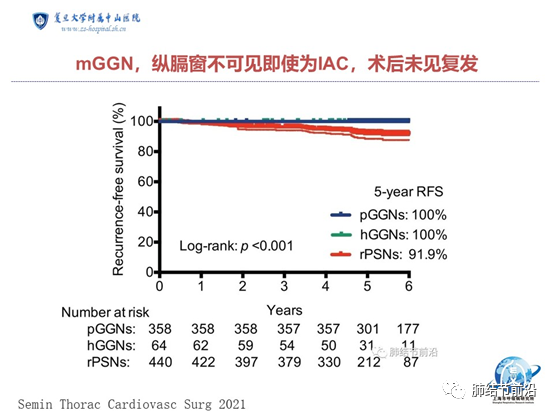
First, for the mixed ground glass nodules that are invisible in the mediastinal window, postoperative recurrence is also rare. According to the data from Shanghai Cancer Hospital, among 358 pure ground glass nodules and 65 mixed ground glass nodules invisible in the mediastinal window, there was no recurrence in 5 years, while 442 mixed ground glass nodules with solid components were visible in the mediastinal window, and the 5-year recurrence rate was 8.1%.

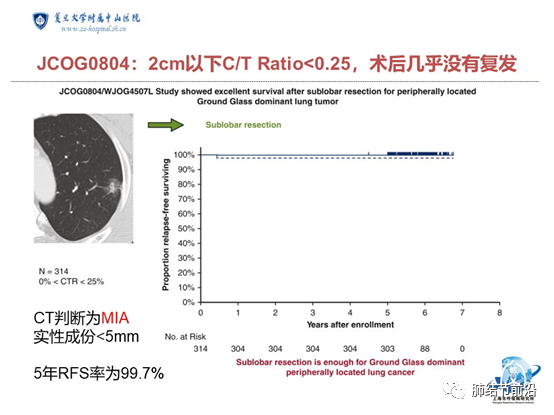
In addition, the recurrence rate of nodules with ctr<0.25 within 2cm is also very low. From the study of jcog0804 in Japan, 314 cases were pathologically diagnosed as AIS, Mia and invasive adenocarcinoma, and only one patient had recurrence five years after operation.
Even the mixed ground glass nodules with ctr<0.5 still have a very good prognosis. According to the data of the Korean study in 2017, the mixed ground glass nodules with ctr<0.5 did not recur 10 years after surgery, even if only sub lobectomy was performed instead of standard lobectomy.
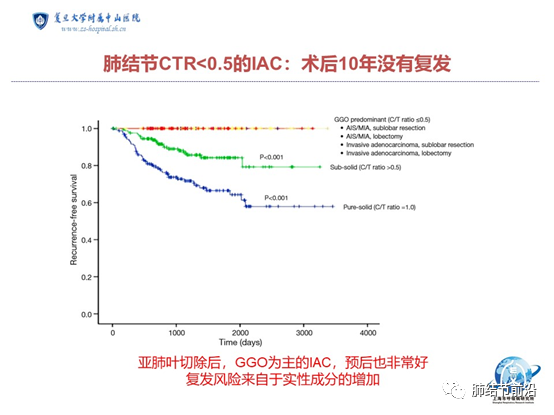
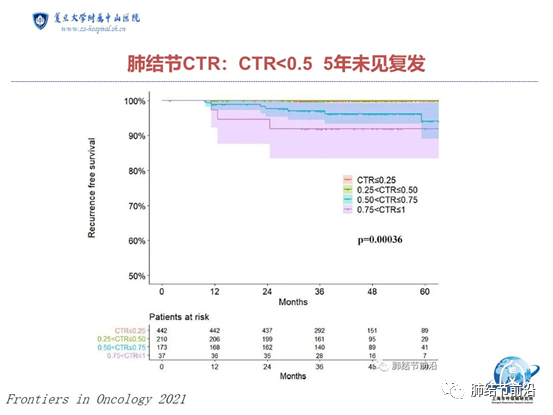
The data of the Department of thoracic surgery of Shanghai Zhongshan Hospital are similar. For pulmonary nodules with ctr<0.5, the recurrence case after 5 years of postoperative observation is 0. The data included 442 cases of mixed ground glass nodules with ctr<0.25 and 210 cases with CTR between 0.25-0.5.
The risk of recurrence mainly comes from the mixed ground glass nodules with ctr>0.5. In the jcog0802 study, the overall 5-year recurrence probability of pulmonary nodules below 2cm and ctr>0.5 was about 12%. The data of Zhongshan Hospital are similar. For pulmonary nodules with ctr>0.5, the 5-year recurrence probability is between 5-8%.
To sum up: the current prognosis of early lung cancer in pulmonary nodules is far better than historical data. In many cases, it does not affect life.
People who will not recur after surgery: carcinoma in situ;
People without recurrence after operation: microinvasive adenocarcinoma;
People with few postoperative recurrence: pure ground glass infiltrating adenocarcinoma, mixed ground glass nodules invisible in the mediastinal window, and mixed ground glass nodules with ctr<0.25;
People with few postoperative recurrence: mixed ground glass nodules with ctr<0.5;
Low probability of postoperative recurrence (5%-12%): people with ctr>0.5.
1.Hu F, Huang H, Jiang Y, et al. 2021. Discriminating invasive adenocarcinoma among lung pure ground-glass nodules: a multi-parameter prediction model. J Thorac Dis. 13(9): 5383-5394.
2.Chen YC, Lin YH, Chien HC, et al. 2021. Preoperative consolidation-to-tumor ratio is effective in the prediction of lymph node metastasis in patients with pulmonary ground-glass component nodules. Thorac Cancer. 12(8): 1203-1209.
3.Xi J, Yin J, Liang J, et al. 2021. Prognostic Impact of Radiological Consolidation Tumor Ratio in Clinical Stage IA Pulmonary Ground Glass Opacities. Front Oncol. 11: 616149.
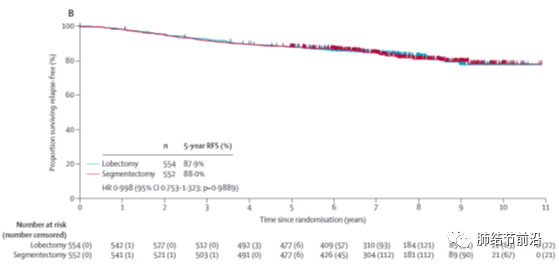
4.Suzuki K, Watanabe SI, Wakabayashi M, et al. 2022. A single-arm study of sublobar resection for ground-glass opacity dominant peripheral lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 163(1): 289-301. e2.
5.Saji H, Okada M, Tsuboi M, et al. 2022. Segmentectomy versus lobectomy in small-sized peripheral non-small-cell lung cancer (JCOG0802/WJOG4607L): a multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised, controlled, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 399(10335): 1607-1617.
Article source:
https://www.medsci.cn/article/show_article.do?id=4e76e32595bf