The excessive accumulation of environmental pollutants in tissues and organs will often cause damage to human body, and eventually lead to the occurrence of various diseases. Due to global climate change, pesticide abuse and industrial development, individuals are often exposed to pollutants from mining and smelting metal ores, pesticide manufacturing and application, wood preservatives, and even drinking water and food intake. There are three common environmental pollutants that need special attention. They are organophosphorus pesticide residues, phthalates from pesticide abuse, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from air pollution, benzo (a) pyrene (BAP) and bisphenol A (BPA) from the plastics industry.
Dicarboxylate is an organophosphorus insecticide. However, many studies have shown that it has adverse effects on mammals. Studies have shown that the carcinogenicity of plasma cholinesterase and formic acid has been reduced. Similarly, BAP is described as a stronger carcinogen than other polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, which can cause DNA damage and play a role in lung cancer and atherosclerosis. BPA is an endocrine disruptor chemical, which can induce tumorigenesis, reproductive toxicity, abnormal immune response and developmental disorders of brain and nervous system through various signal pathways.
Recently, people have increasingly recognized the important link between pollutant accumulation and health. So far, different methods have been developed to remove these pollutants, including biodegradation and non biodegradation. Well known methods include degradation (chemical or microbial) or adsorption on different types of materials. However, the elimination of pollutants that have abnormally accumulated in the human body has not been reported.
It is reported that physical exercise is an effective non drug intervention for human health. Exercise has also been shown to treat many chronic diseases by changing metabolism, strengthening muscles and improving immunity. Physical exercise is considered part of a healthy lifestyle. Individuals who exercise regularly can get positive feedback from their environmental and social contacts, which is even good for the treatment of mental diseases. Marisa tours assessed the effect of exercise on patients with depression within 12 weeks of exercise enhancement and found that the titer symptoms of exercise in the treatment of depression were improved, which was closely related to the overall outcome.
Similarly, obesity, hyperlipidemia, metabolic syndrome, polycystic ovary syndrome, type 2 diabetes, type 1 diabetes and other metabolic diseases have also been reported. In a clinical study, postprandial moderate exercise in patients with type 2 diabetes reduced the peak blood glucose, mean blood glucose and peak blood glucose levels after 2 hours compared with the control group. In addition, regular physical exercise can induce anti atherosclerotic adaptation of vascular function and structure, improve myocardial regeneration and cardiac parasympathetic regulation. In addition, physical exercise can also improve the lung function and quality of life of patients with malignant tumors. Exercise can also reduce mortality associated with air pollution. However, little is known about the extent to which the elimination of environmental pollutants can be attributed to physical exercise.
Here, we recruited 200 people to receive physical exercise for 3 months to evaluate the correlation between the improvement effect of pollutants and different physical exercise. More importantly, identifying the most important factors that can affect the improvement of physical exercise interventions may provide new insights into the elimination of pollutants in young people.
A total of 200 people were recruited to choose different types of exercises according to their wishes β Glucuronidase hydrolysis measures the level of urinary pollutants. The exercise program lasted for 3 months, three times a week, 90 minutes each time. After the subjects chose their own preference exercise during leisure, they were not allowed to participate in any other exercise. Sports include basketball, volleyball, table tennis, handball, tennis, football, badminton, Latin dance, rhythmic gymnastics, bodybuilding, yoga and shaping. The subjects of Hohai University took a 90 minute course. Monitor heart rate (HR) before and after exercise. The first 30 minutes of exercise are the warm-up period, in which the speed gradually increases, and the moderate severity of aerobic exercise is equal to 60-70% of the maximum hr. After that, 10 minutes of cooling includes stretching exercise of lower limb muscles and whole body relaxation for 1 minute.
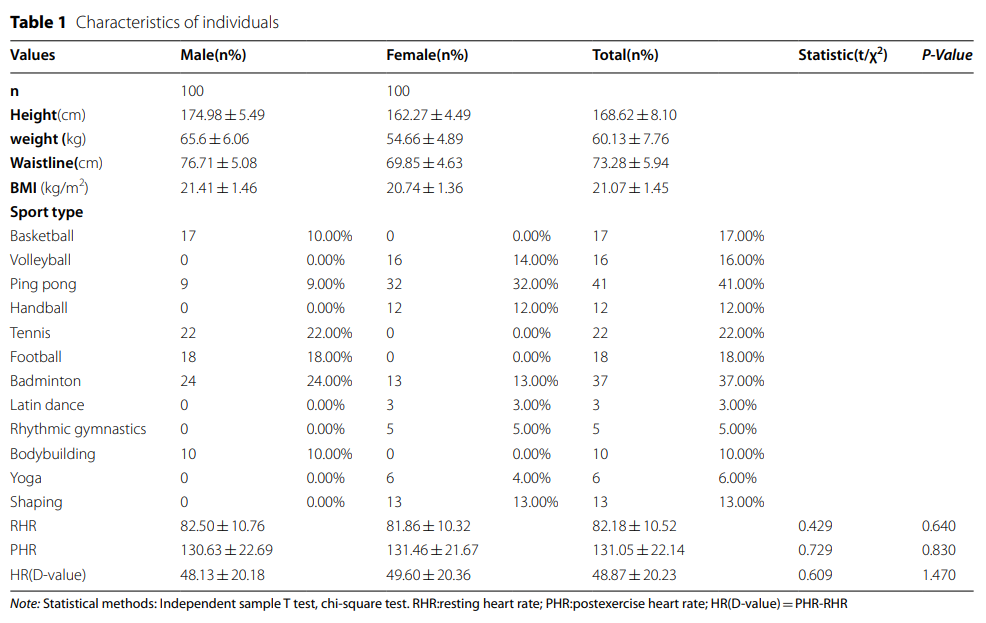
1. After physical exercise, the levels of three environmental pollutants have decreased
The levels of dicarboxylate, BAP and BPA in 200 individuals before and after 3 months of exercise were measured by high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Overall, after physical exercise, the levels of dicarboxylate, BAP and BPA (8.06 ± 1.51 ng / ml, 0.32 ± 0.08 pg / ml, 3.19 ± 0.54 ng / ml) were lower than those before exercise (10.78 ± 1.37 ng / ml, 0.4 ± 0.05 pg / ml and 4.07 ± 0.38 ng / ml), respectively, with significant differences (Table 2).
In addition, the influence of gender on pollutant elimination is also analyzed. There was no significant difference in the elimination of dicarboxylate between men and women (Fig. 1a). The elimination of BaP was higher in women than in men (Fig. 1b), however, the elimination of BPA was higher in men than in women (Fig. 1c).
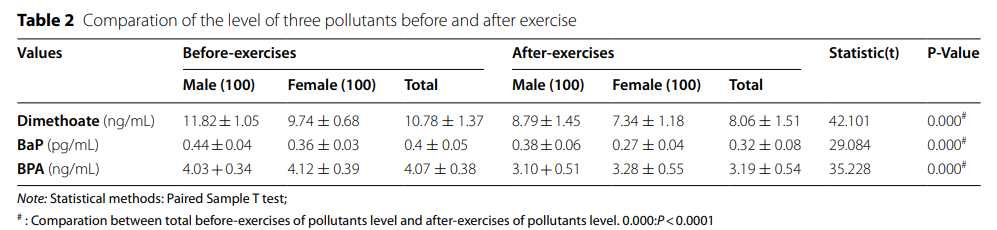

2. The influence of gender preference and physical exercise on the elimination of pollutants
Due to gender differences, men and women have preferences in the choice of physical exercise. For statistical analysis, we selected more than 8 subjects from 12 sports for analysis. Although there was no statistical difference in the improvement effect of football and other male preference exercises, basketball showed the best elimination potential (Fig. 2a, c), football had the worst elimination potential for dicarboxylate and BPA, but football had the greatest elimination potential for BAP (Fig. 2b). All men's preference for physical exercise showed that the exclusion potential of dicarboxylate was the best and that of BaP was the worst (Fig. 2D).
Interestingly, the elimination potential trend of the five female preferred sports to the three pollutants is the same, but there is no statistical difference (Fig. 2E-G). In contrast, all female preferred sports showed the best elimination potential for BAP (Fig. 2H). In the common preference exercise, the same elimination trend was observed, in which the elimination trend of BaP was the best (Fig. 2J), while there was no difference between the elimination trend of dicarboxylate and BPA (Fig. 2I, K). Male preference for physical exercise, female preference for physical exercise and common preference for physical exercise are defined according to gender preference (Fig. 2L). In addition, we divided 12 sports into indoor (table tennis, handball, badminton, Latin dance, rhythmic gymnastics, fitness, yoga and shaping) and outdoor sports (basketball, volleyball, tennis and football), and investigated the elimination potential of three pollutants by different gender. The results showed that there was no significant difference in the improvement of dicarboxylate and BPA between men and women (Fig. 2m, n), but women seemed to have a better level of BaP pollutants in indoor and outdoor sports (Fig. 2O).

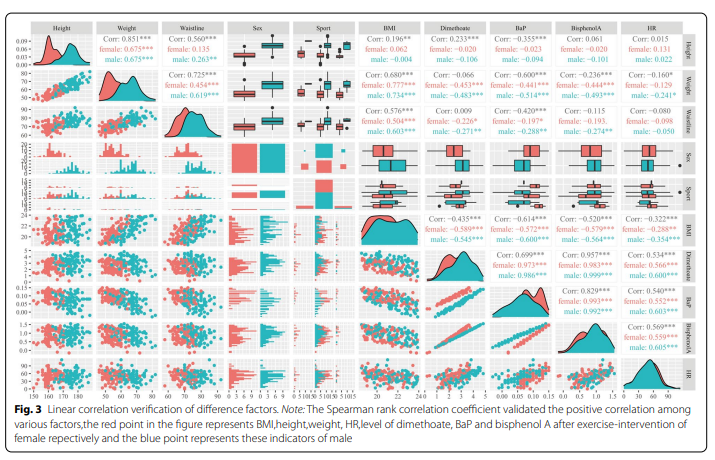
3. Linear correlation verification of difference factors
The difference factors were verified by linear correlation: there was no significant correlation between the difference values of height, weight, waist circumference, dicarboxylate, BAP, BPA and HR in male and female subjects. There was a high correlation between BMI and the levels of dicarboxylate, BAP and BPA after exercise intervention. BMI was correlated with height, weight and waist circumference, but there was no significant correlation between exercise type and heart rate and rest index (Fig. 3).
4. Multiple ordered logic and logistic regression analysis
Table 3 shows the predictors of different outcomes using multivariate ordered logic and logistic regression analysis. The results showed that the change degree of HR was the risk factor affecting the elimination of dicarboxylate, BAP and BPA, and the influence degree of the three pollutants was the same. BMI is a protective factor affecting the clearance of dicarboxylate, BAP and BPA. The lower BMI, the more obvious the elimination of pollutants, and the difference was statistically significant. Gender also affects the elimination of these pollutants. However, the type of physical exercise has no significant effect on the elimination of the three pollutants.

To sum up, these research results show that physical exercise is a novel and effective method to reduce the level of pollutants in adolescents, which helps us understand the health benefits of physical exercise, and can provide a reference for promoting young people to actively participate in physical exercise with the best elimination potential of pollutants. So as to form the habit of regular physical exercise and improve self-health ability and physical health level. However, due to the insufficient sample size of each physical exercise, we did not get a satisfactory result, that is, the elimination potential of different physical exercise on the three pollutants. Therefore, due to the small sample size and the lack of long-term follow-up study, it is necessary to further expand the sample size of follow-up study.
Original source:
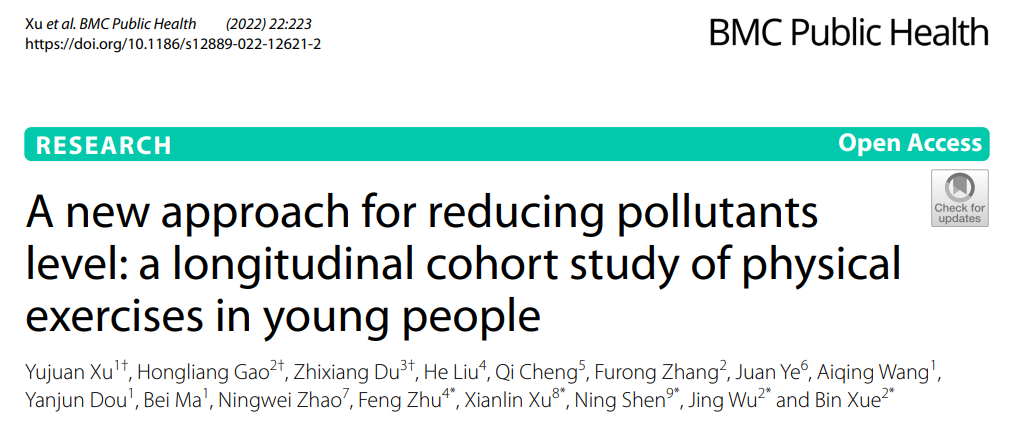
Xu et al.A new approach for reducing pollutants level: a longitudinal cohort study of physical exercises in young people.
BMC Public Health (2022) 22:223
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-12621-2.
Article source:
https://www.medsci.cn/article/show_article.do?id=81f52952188e