Previous studies on patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D) have found that the incidence rate of some cancers in this population is higher than that in the general population. However, no studies have evaluated risk factors for the incidence rate of T1D cancer. In this study, researchers used data from the diabetes control and complications test (DCCT) and the diabetes intervention and complications Epidemiology (EDIC) study to explore the association between risk factors and cancer incidence rate in patients with T1D during the 28 year follow-up period.
DCCT included 1441 patients from 29 clinical trial institutions in North America. The data were collected from 1983 to 1989. By the end of DCCT in 1993, 1375 surviving subjects continued to participate in the EDIC study. As of 2012, a total of 1304 patients had complete and updated data on the incidence of cancer each year.
The researchers grouped the participants according to the daily average insulin dose level: low dose: <0.5 unit /kg; Medium dose: 0.5~0.8 unit /kg; High dose: ≥ 0.8 unit /kg. The research data showed that during the follow-up period of 33813 person years, 93 (7%) of the 1303 patients in the final analysis were diagnosed with cancer, and the cancer incidence rate was 2.8 (95%ci, 2.2-3.3) /1000 person years. The average age of the first diagnosis of cancer was 50 years old, and the average course of diabetes was 25 years.
Among the 93 patients diagnosed with cancer, 57 (61%) were women. Cancer was diagnosed in 8 cases (9%) within 10 years of follow-up, 31 cases (33%) during 11-20 years, and 54 cases (58%) during 21-28 years. The results showed that the incidence rate of cancer increased with age in patients with type 1 diabetes, and the age risk ratio (HR) was 1.08 (95%ci, 1.05-1.12); The female incidence rate also increased, and the female sex HR was 1.74 (95%ci, 1.15-2.64).
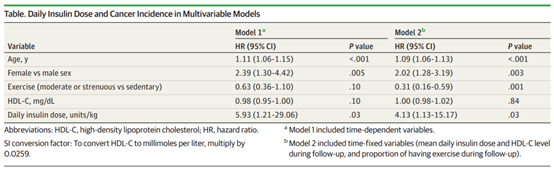
After adjusting for age and gender factors, the analysis data showed that other variable factors, including exercise habits and HDL-C levels, were negatively correlated with cancer incidence rate; Daily insulin dose is positively correlated with cancer risk. In addition, there is no correlation between traditional metabolic factors, such as obesity, blood glucose control level, blood pressure control level and cancer risk.
It is noteworthy that the association between daily insulin dose (especially high dose) and cancer risk is more obvious than age and gender, and daily insulin dose is significantly correlated with increased cancer risk (model 1:hr=5.93; 95%ci, 1.21-29.06; model 2:hr=4.13; 95%ci, 1.13-15.17).
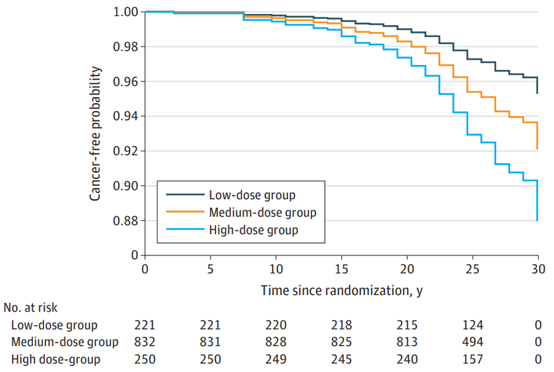
The incidence rate of cancer in low, medium and high-dose average insulin groups were 2.11/1000 person years, 2.87/1000 person years and 2.91/1000 person years respectively. Patients in the high-dose group had a higher risk of cancer than those in the low-dose group.
In general, the results of this study suggest that daily insulin dose is associated with the risk of cancer in patients with type 1 diabetes, and the risk of high-dose group is significantly higher than that of low-dose group. This study is also the first study to explore cancer-related risk factors in type 1 diabetes.
Source of original text:
Zhong W, Mao Y. Daily Insulin Dose and Cancer Risk Among Patients With Type 1 Diabetes. JAMA Oncol. Published online July 28, 2022. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2022.2960
Article link:
https://www.medsci.cn/article/show_article.do?id=d323e3419822













